Search ELISA Kits
Protease Proteins Types
-
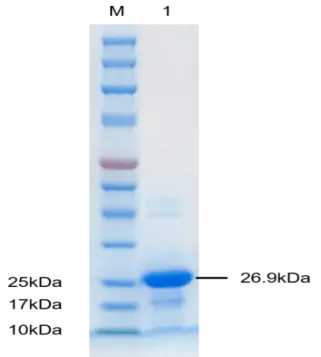
PGEU0001P-T SUMO protease (Ulp1) protein, Recombinant
Cat. No.: PGEU0001P-T
Uniprot No.: Q02724
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression region: Lys401-Lys621
Fusion Tag: 6×His (C-terminus)
Protease Proteins FAQs
-
Q
What is a protease protein?
Protease is the general term for a class of enzymes that hydrolyze protein peptide chains. It can be said that the protein is broken into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids to promote the formation of new protein products. It mainly hydrolyzes polypeptide bonds in proteins by breaking covalent bonds. It plays a role in a variety of biological functions, including digestive proteins, protein metabolism and cell signaling.
-
Q
What is the fuction of protease protein?
Proteases play many roles in physiology, biochemistry and cell or organism. Proteases can destroy protein polypeptide bonds. According to their functions, they can be divided into acidic, neutral and alkaline proteases and are widely distributed in plants, animals and microorganisms. Even in a variety of conditions, such as high salt, high temperature and strong ion environment, they all exist. For example, trypsin has an anti-tumor activity for screening natural drugs in vitro. In sample treatment, alkaline phosphatase can remove the soft tissue of bone samples. In food, flavor protease, protamex and papain have the potential to decompose fungus food to produce different tastes and nutritional values. In the process of pretreatment against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, inhibition of calpain activity can protect the intimal membrane of the cardiac tube. It can reduce the cell membrane damage of ischemia-reperfusion myocardium.


_00(1).webp)