Search ELISA Kits
Chicken ELISA Kits Types
-
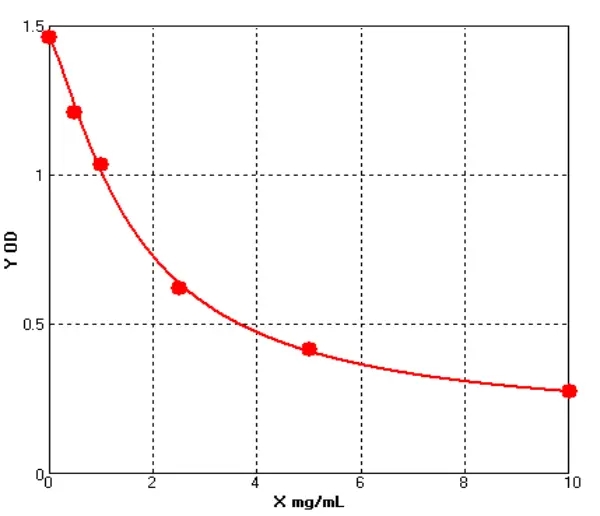
Chicken Acetoacetyl CoA synthetase ELISA kit (E12A0083)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12A0083
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
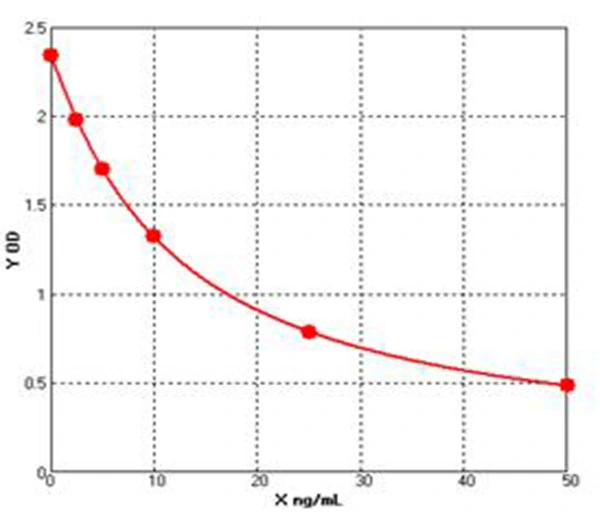
Chicken Tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand ELISA kit (E12T0023)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12T0023
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
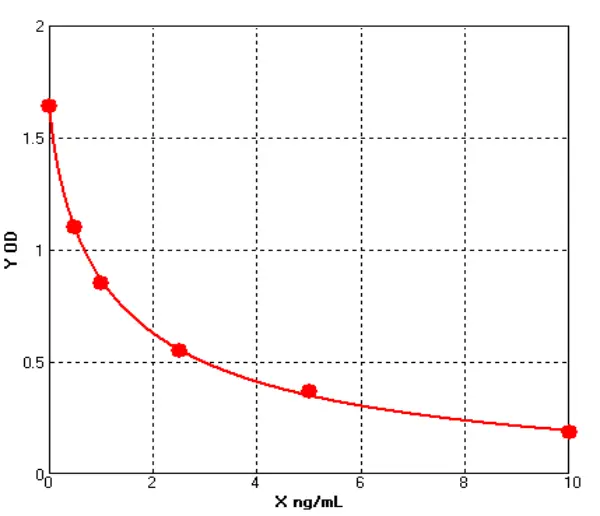
Chicken Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 ELISA kit (E12V0004)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12V0004
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
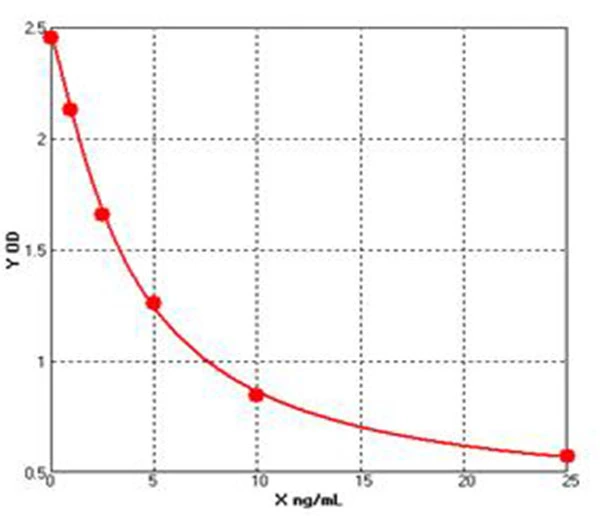
Chicken Total Adiponectin ELISA kit (E12A0125)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12A0125
Detection Range: 1.0-25ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
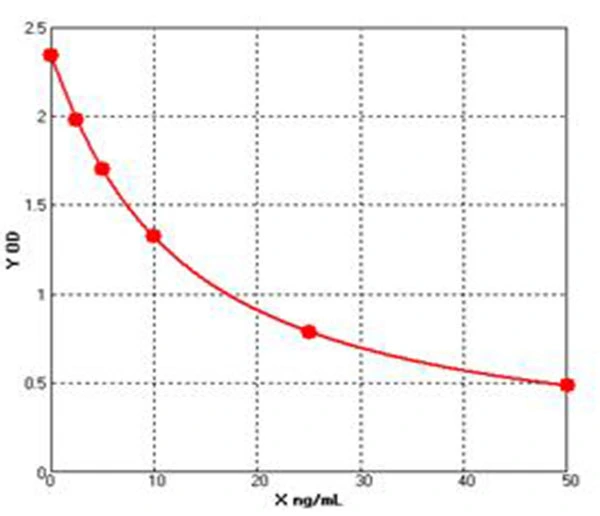
Chicken BCL2 Associated X Protein ELISA kit (E12B0032)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12B0032
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
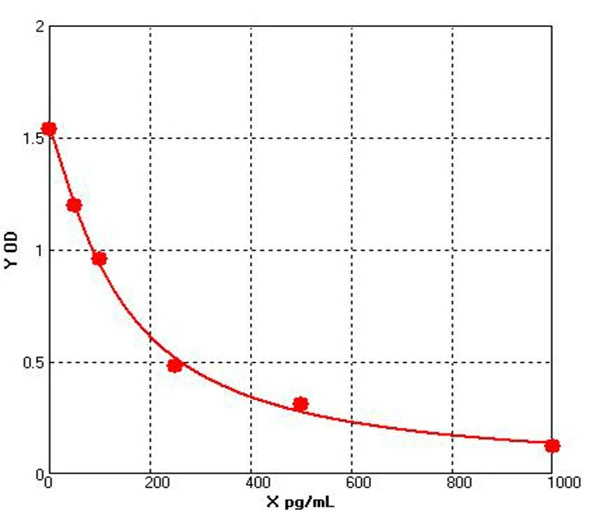
Chicken β Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma 2 ELISA kit (E12B0033)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12B0033
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml
-
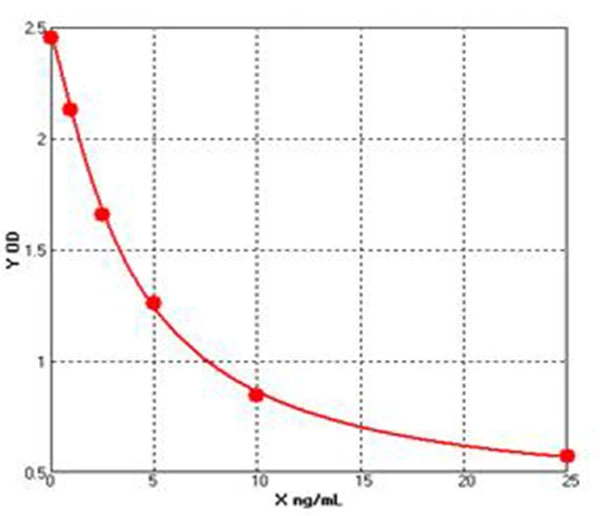
Chicken Bcl 2 like protein 1 ELISA kit (E12B0764)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12B0764
Detection Range: 1.0-25ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
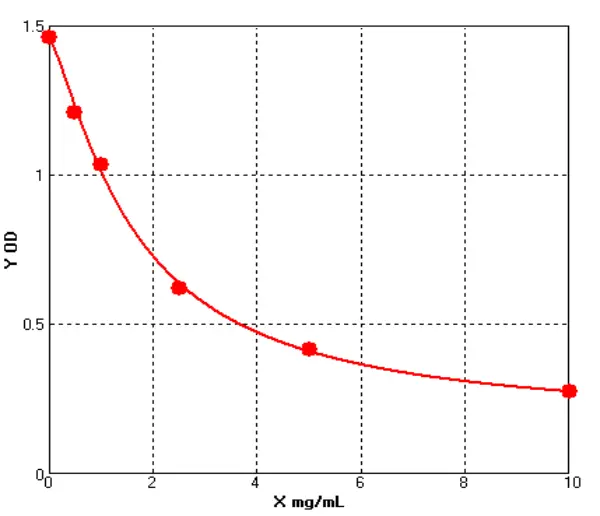
Chicken Immunoglobulin A ELISA kit (E12I0021)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0021
Detection Range: 0.5-10mg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1mg/mL
-
Chicken Cluster of Differentiation 4 ELISA kit (E12C0004)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12C0004
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
Chicken Cytochrome P450 ELISA kit (E12C0863)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12C0863
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
Chicken Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate ELISA kit (E12G0003)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12G0003
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
Chicken Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase ELISA kit (E12C0903)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12C0903
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
Chicken Prostaglandin E2 ELISA kit (E12P0012)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12P0012
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
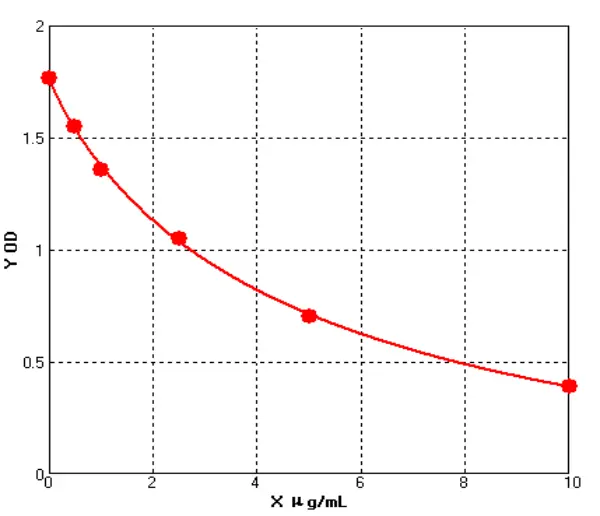
Chicken Superoxide Dismutase ELISA kit (E12S0012)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12S0012
Detection Range: 0.5-10ug/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ug/mL
-
Chicken Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin ELISA kit (E12S0004)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12S0004
Detection Range: 0.5-10ug/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ug/mL

-
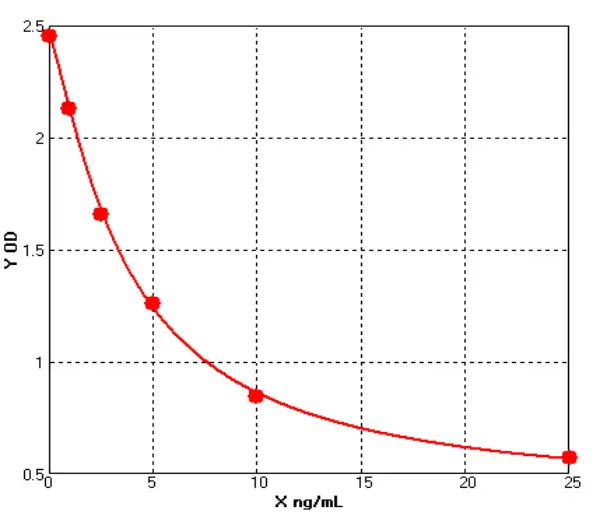
Chicken Epidermal growth factor Like Domain Protein, Multiple 7 ELISA kit (E12E0406)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12E0406
Detection Range: 1.0-25ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
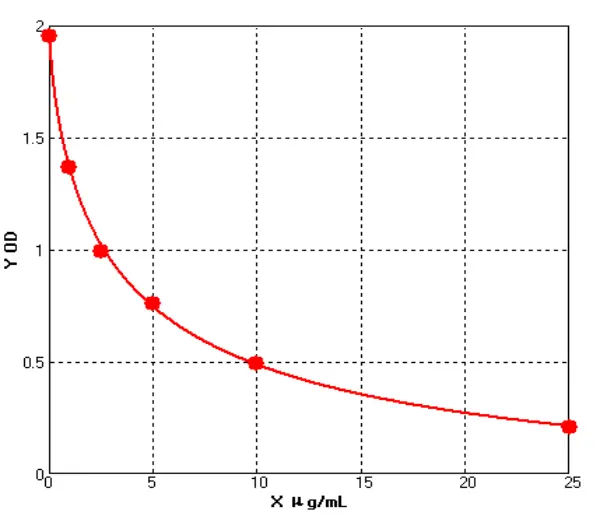
Chicken Macromolecule Adiponectin ELISA kit (E12M0038)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12M0038
Detection Range: 1.0-25ug/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ug/mL
-
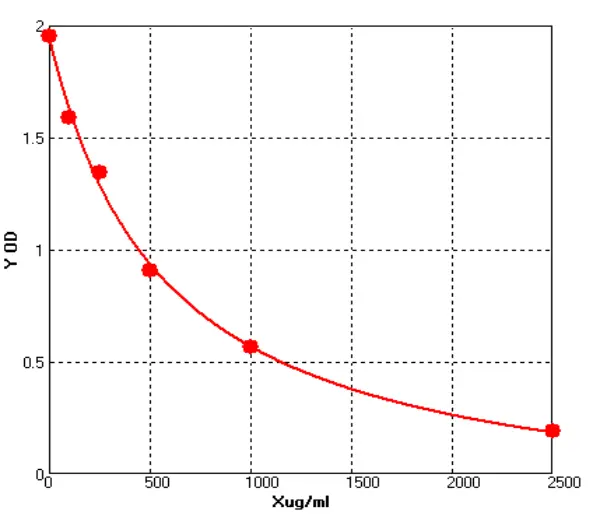
Chicken Immunoglobulin M ELISA kit (E12I0038)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0038
Detection Range: 100-2500ug/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ug/mL
-
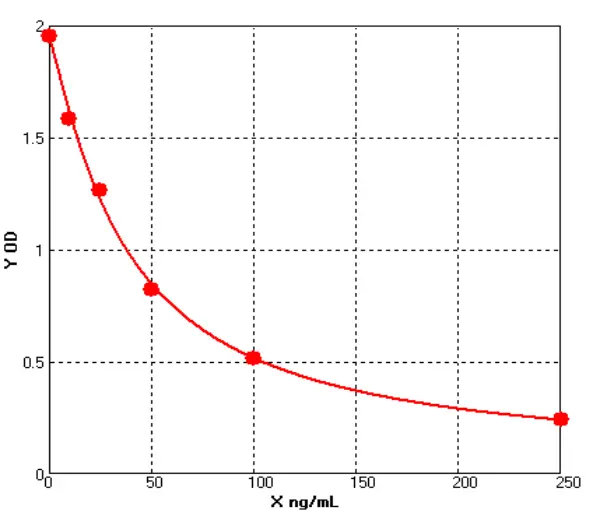
Chicken Glutamine synthetase ELISA kit (E12G0012)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12G0012
Detection Range: 10-250ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL
-
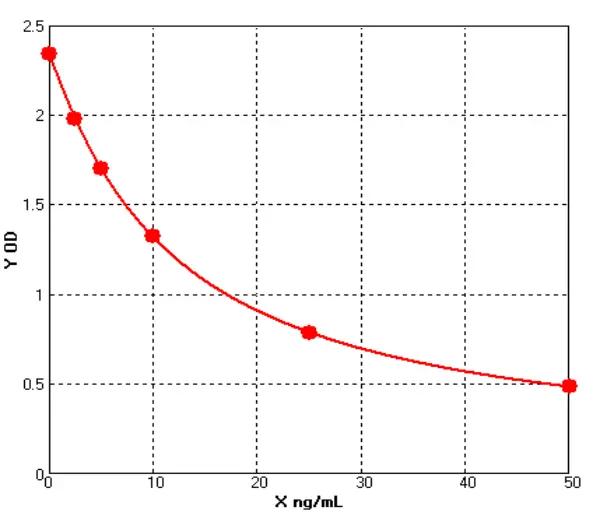
Chicken Soluble Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 ELISA kit (E12S0258)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12S0258
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
Chicken Matrix metalloproteinase 9 ELISA kit (E12M0329)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12M0329
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
Chicken Cluster of Differentiation 8 ELISA kit (E12C0007)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12C0007
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
Chicken Osteocalcin ELISA kit (E12O0001)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12O0001
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
Chicken Progesterone ELISA kit (E12P0200)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12P0200
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL

-
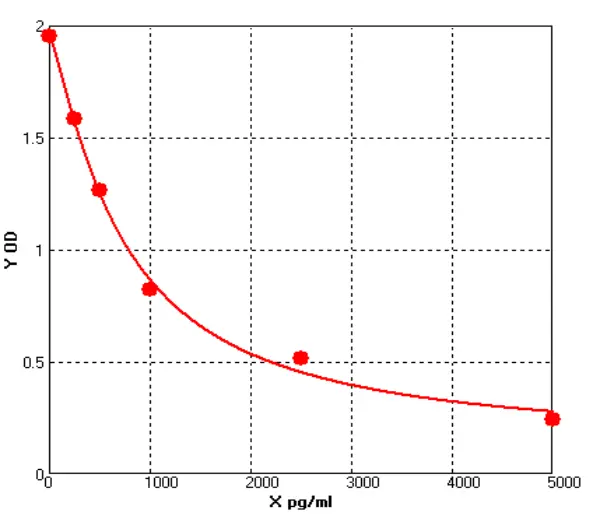
Chicken Phospholipase A2, Secreted ELISA kit (E12S0173)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12S0173
Detection Range: 250-5000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0 pg/mL
-
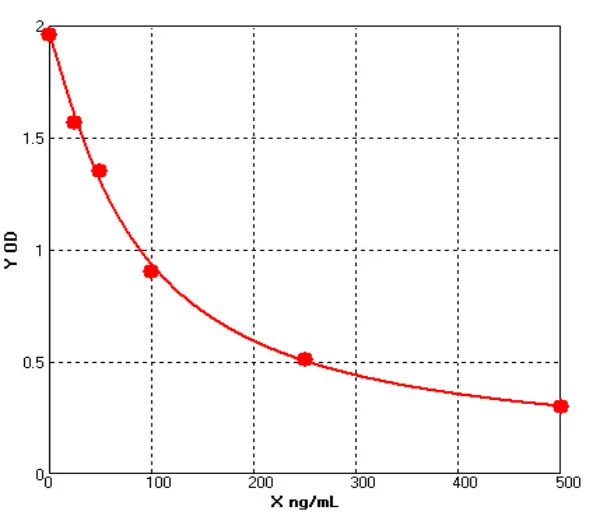
Chicken Collagen Type Ⅲ ELISA kit (E12C0017)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12C0017
Detection Range: 25-500ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0 ng/mL
-
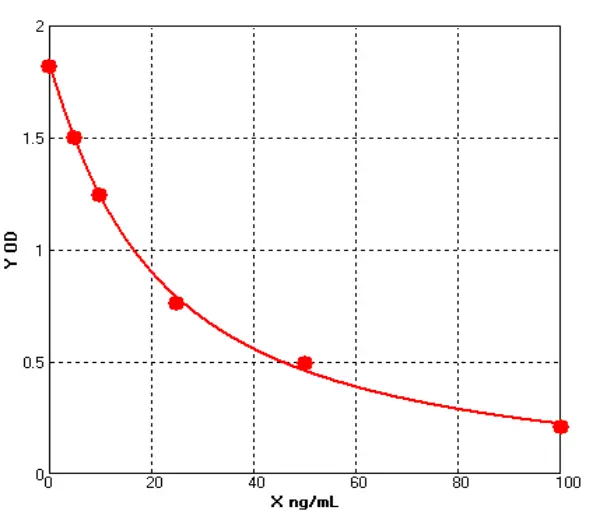
Chicken 72 kDa type IV collagenase ELISA kit (E12M0445)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12M0445
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL
-
Chicken Anti Endothelin 1 ELISA kit (E12E0177)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12E0177
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL

-
Chicken Free cholesterol ELISA kit (E12F0212)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12F0212
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL

-
Chicken Inducible nitric oxide synthase ELISA kit (E12I0396)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0396
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL

-
Chicken Serotonin Transporter ELISA kit (E12S0089)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12S0089
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL

-
Chicken Protein kinase A ELISA kit (E12P0746)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12P0746
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL

-
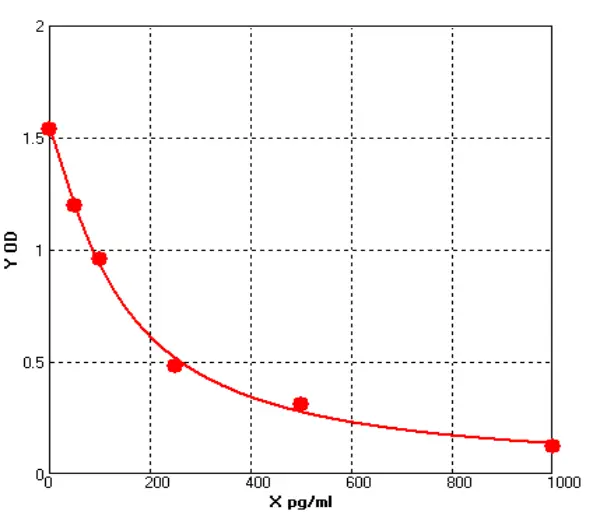
Chicken Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha ELISA kit (E12T0008)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12T0008
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL
-
Chicken Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor ELISA kit (E12V0010)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12V0010
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor ELISA kit (E12G0112)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12G0112
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor ELISA kit (E12G0016)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12G0016
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interferon γ ELISA kit (E12I0345)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0345
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interleukin 10 ELISA kit (E12I0023)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0023
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interleukin 12 ELISA kit (E12I0033)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0033
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interleukin 15 ELISA kit (E12I0357)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0357
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interleukin 1β ELISA kit (E12I0010)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0010
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interleukin 2 ELISA kit (E12I0308)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0308
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interleukin 4 ELISA kit (E12I0007)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0007
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Interleukin 6 ELISA kit (E12I0006)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0006
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
Chicken Parathyroid hormone receptor ELISA kit (E12P0353)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12P0353
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
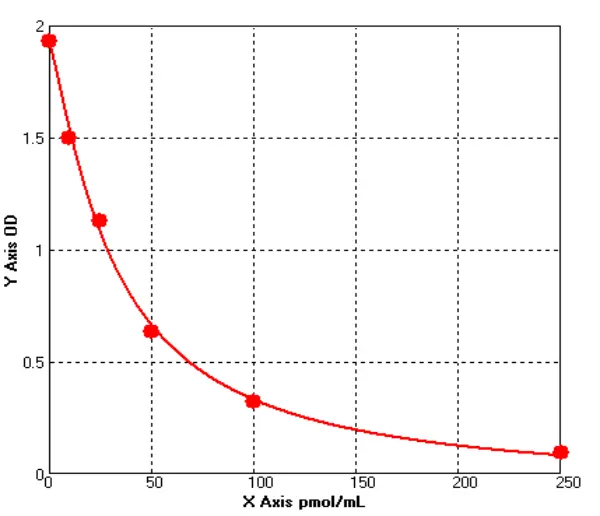
Chicken cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate ELISA kit (E12C0027)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12C0027
Detection Range: 10-250pmol/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0pmol/ml
-
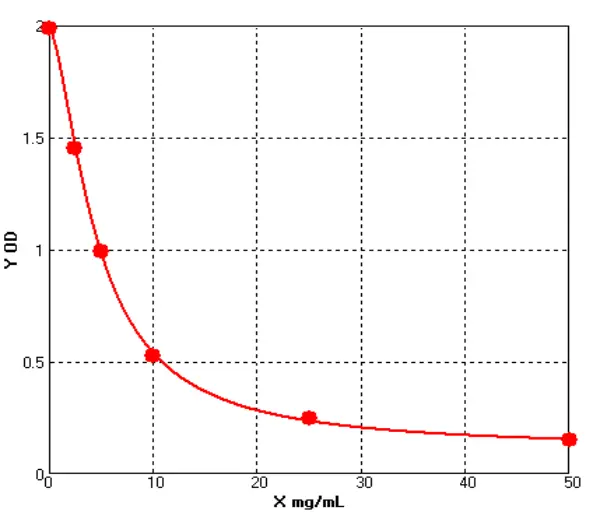
Chicken Immunoglobulin G ELISA kit (E12I0058)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0058
Detection Range: 2.5-50mg/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1mg/mL
-
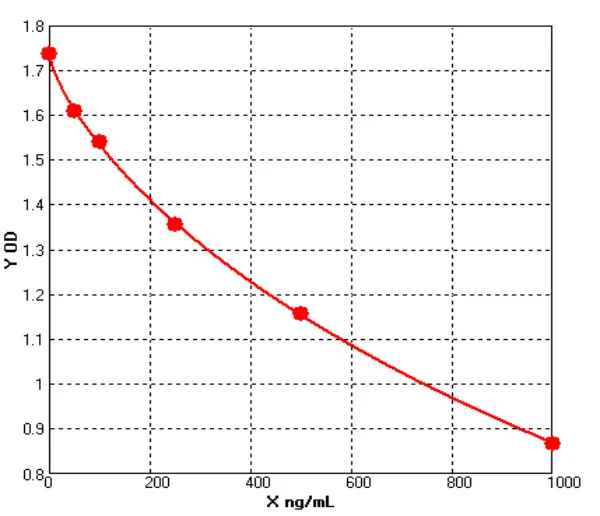
Chicken Collagen Type I ELISA kit (E12C0014)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12C0014
Detection Range: 50-1000ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/mL
-
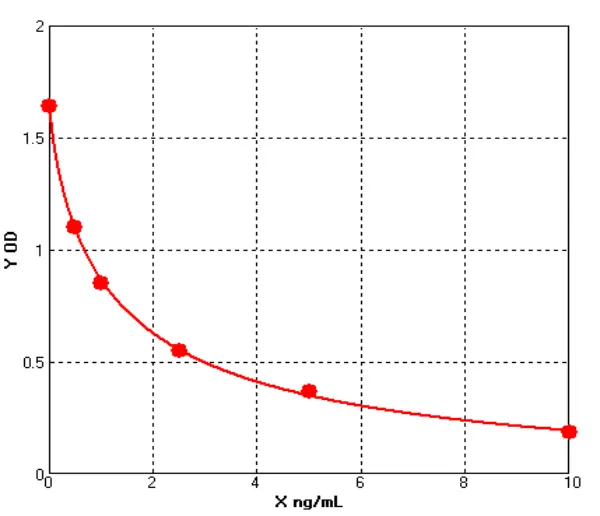
Chicken Nuclear factor kB ELISA kit (E12N0011)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12N0011
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
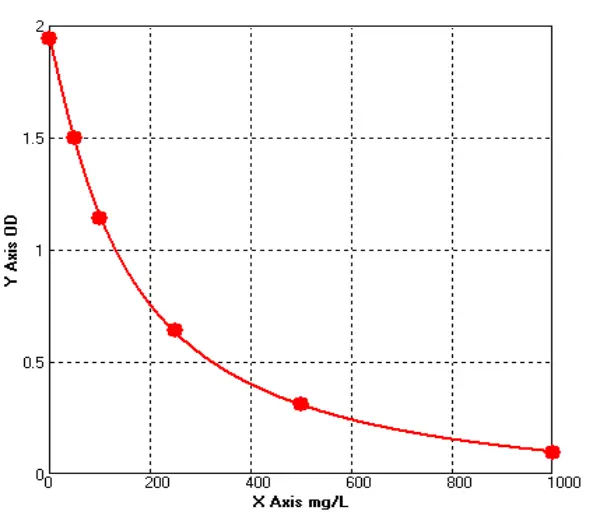
Chicken Immunoglobulin A1 ELISA kit (E12I0016)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E12I0016
Detection Range: 50-1000mg/L
Reactivity: Chicken
Sensitivity: 1.0mg/L
What Are the Relevant Indicators of Infectious Diseases in Chickens?
Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) in chickens is a highly contagious disease. The virus is transmitted through the environment, feed, etc. It can mix infection or secondary infect with Newcastle Disease, chronic respiratory disease, colibacillosis, and other diseases. The bursal disease infection can cause severe immunosuppression. Avian infectious rhinitis is caused by haemophilus parahaemophilus, which can delay the spawning period, mix infection in septicemia, lead to the induction of its activity and cause chronic respiratory diseases. Chicken Pullorum Disease is caused by salmonella, which is infected through the digestive tract, and this disease is limited to the reproductive system. Mild influenza in chickens is caused by the H9 virus with low pathogenicity. And the mortality rate and loss degree are related to the degree of secondary colibacillosis. Most of the above chicken diseases were diagnosed by serology.
Can Other Bird Samples Be Tested with Chicken Kits? Why? (Are there Any Homologies?)
No. In the classification of animals, birds belong to the animals about classes, and chickens belong to the animals about species, which are both warm-blooded and egg-laying, and both breathe with lungs. The main characteristics of birds are: streamlined bodies (spindle type), feathery body surfaces, and the forelimbs generally become wings (some species have wings degenerated), well-developed pectoral muscles, short rectum, large appetites, fast digestions (well-developed digestive systems), which helps to reduce weight and facilitate flight. Their hearts have two atria and two ventricles, and the heartbeats are fast. Body temperature is constant. In addition to the lungs, the respiratory organs also have airbags formed by protruding lung walls to help the lungs double breathe. Galliformes is located in a basic branch of the bird evolutionary tree, the classification system of DNA hybridization technology, and the 14-year classification system based on whole genome sequencing, which confirmed that they are closely related to Yaniformes. They also belong to the small classes of chicken and goose. Combining ND2, cyt b genes, and other nuclear genes, Galliformes can be divided into 7 families. Therefore, chickens and birds are not identical, and their samples are quite different.