Search ELISA Kits
Canine ELISA Kits Types
-
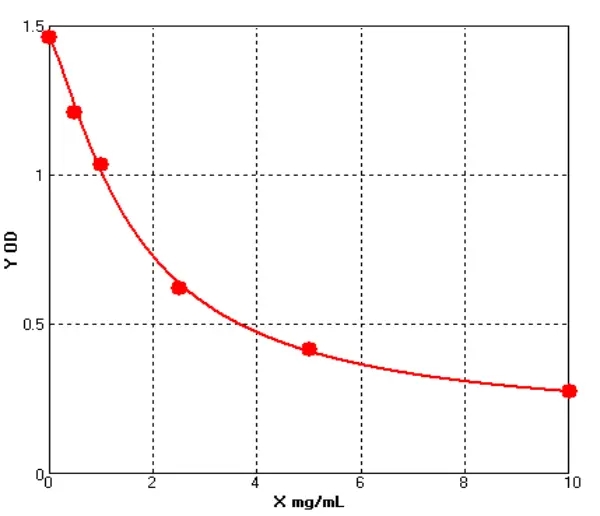
Canine Aggrecan ELISA kit (E08A0413)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08A0413
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
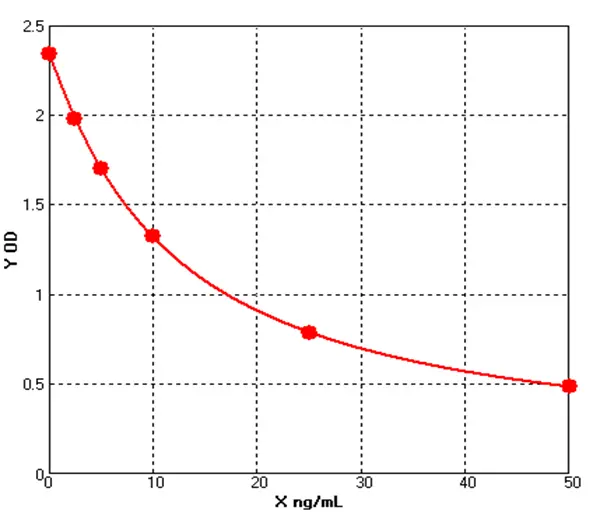
Canine Aquaporin 4 ELISA kit (E08A0467)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08A0467
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
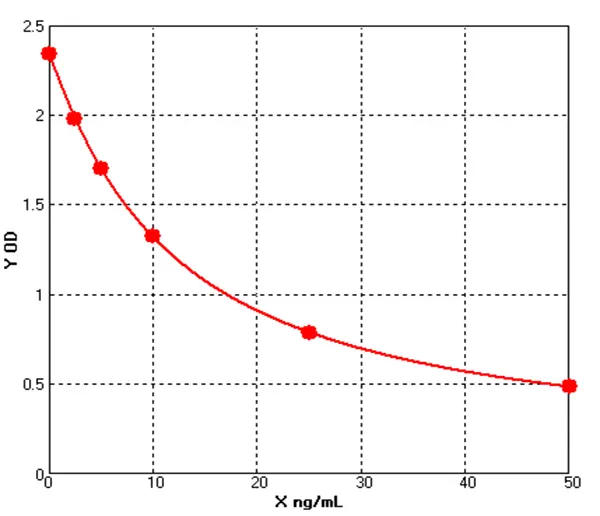
Canine Activin A ELISA kit (E08A0643)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08A0643
Detection Range: 50-1000 pg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL
-
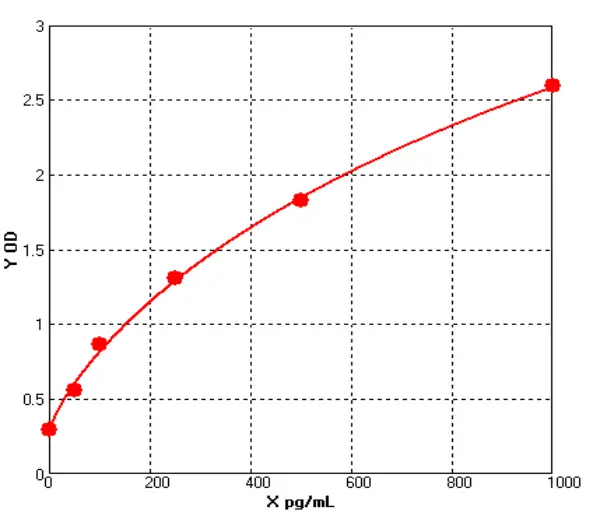
Canine Transforming Growth Factor β1 ELISA kit (E08T0009)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08T0009
Detection Range: 50-1000 pg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL

-
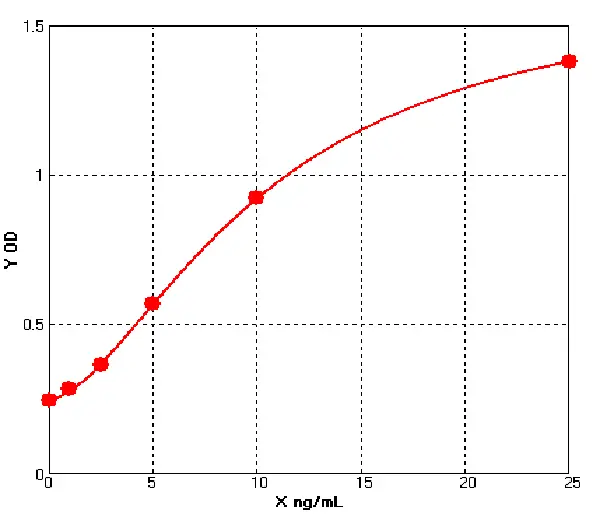
Canine Matrix metalloproteinase 9 ELISA kit (E08M0329)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08M0329
Detection Range: 1.0-25 ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
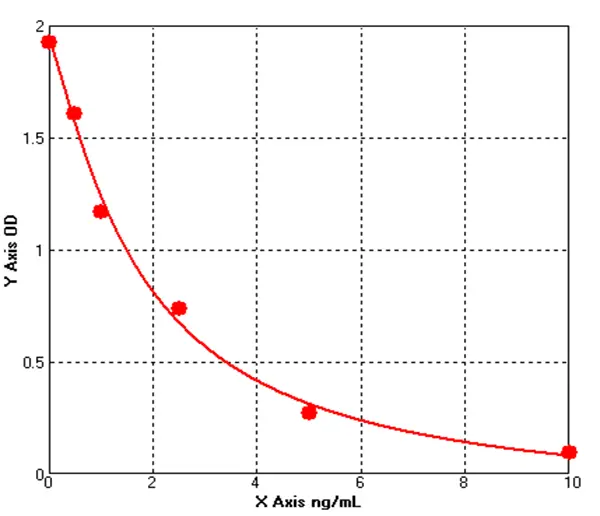
Canine 26S Proteasome ELISA kit (E08A0669)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08A0669
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
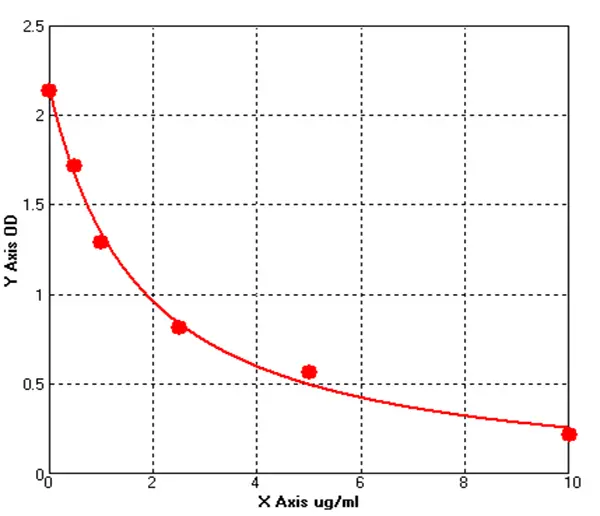
Canine Apoprotein B100 ELISA kit (E08A0851)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08A0851
Detection Range: 0.5-10 μg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ug/mL
-
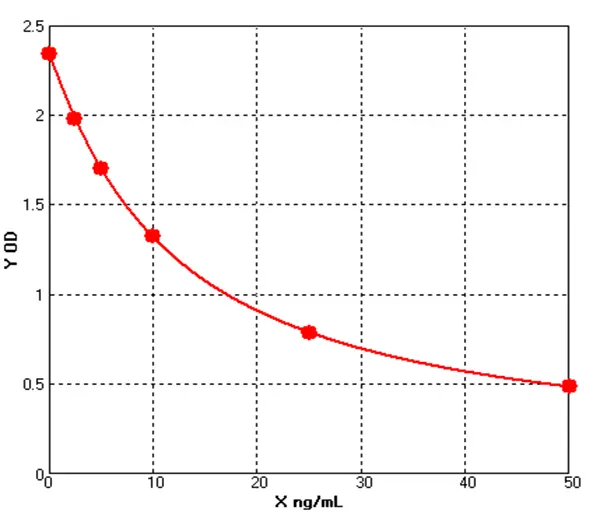
Canine Aquaporin 1 ELISA kit (E08A0863)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08A0863
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
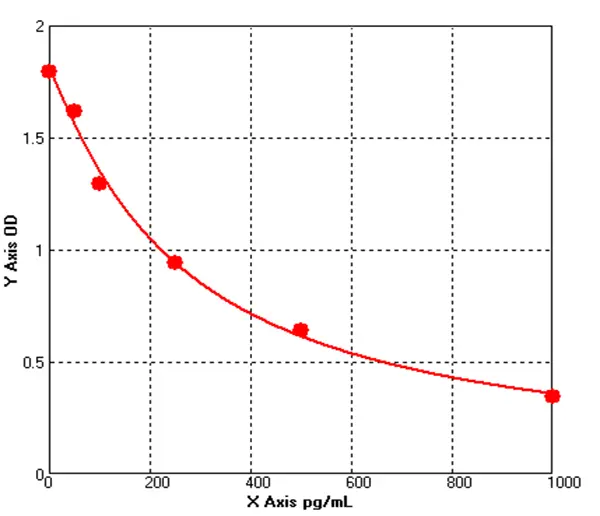
Canine Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor ELISA kit (E08B0029)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08B0029
Detection Range: 50-1000 pg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/mL
-
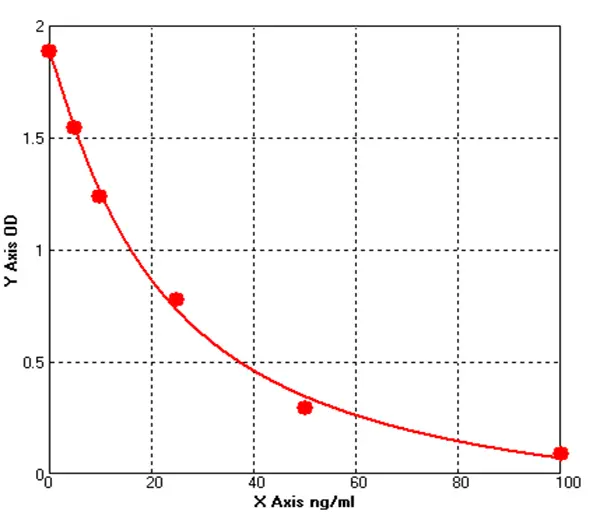
Canine BCL2 Associated X Protein ELISA kit (E08B0032)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08B0032
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/ml
-
Canine Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 ELISA kit (E08M0016)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08M0016
Detection Range: 5.0-100ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/ml

-
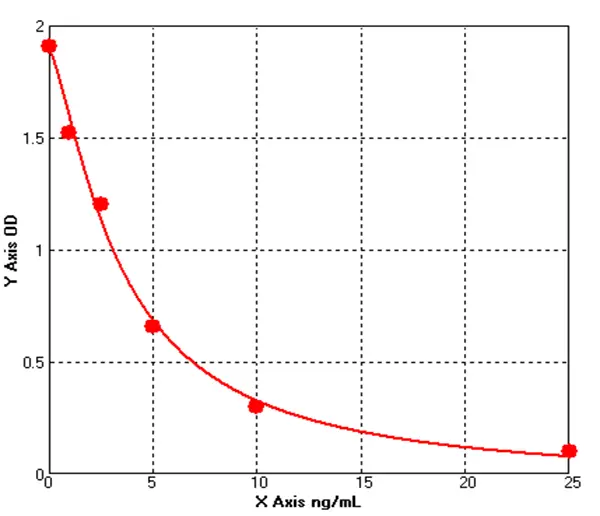
Canine β Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma 2 ELISA kit (E08B0033)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08B0033
Detection Range: 1.0-25ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
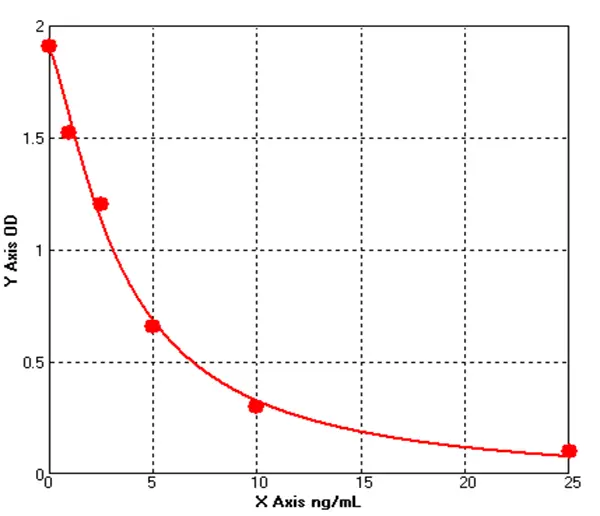
Canine Caspase 9 ELISA kit (E08C0096)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08C0096
Detection Range: 1.0-25ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
Canine Collagen Type II Alpha 1 ELISA kit (E08C0323)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08C0323
Detection Range: 10-250ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/ml
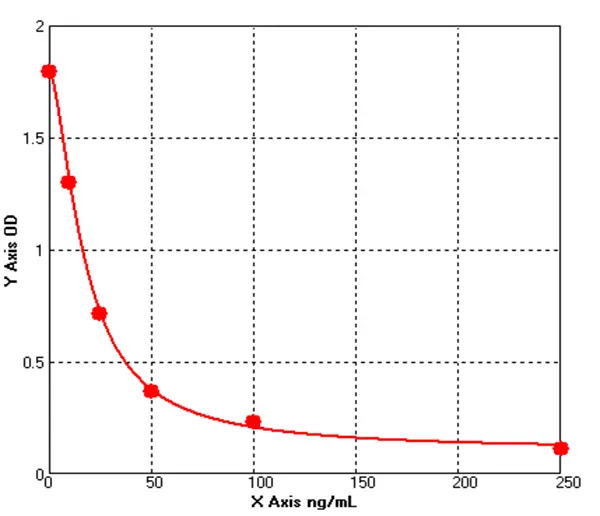
-
Canine Caspase 3 ELISA kit (E08C0549)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08C0549
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
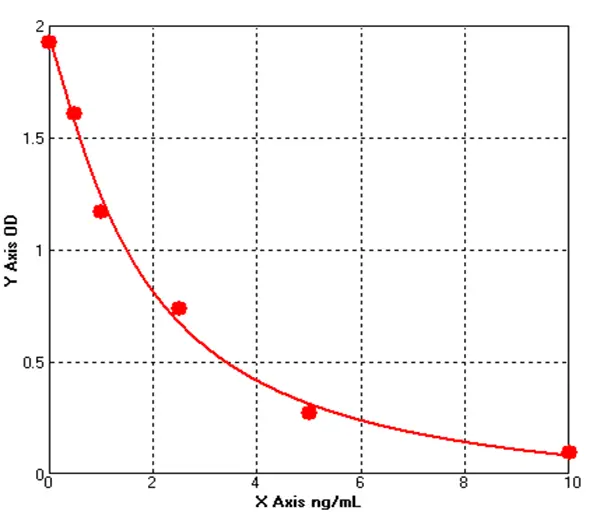
-
Canine Ferritin ELISA kit (E08F0010)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08F0010
Detection Range: 25-500ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0 ng/mL
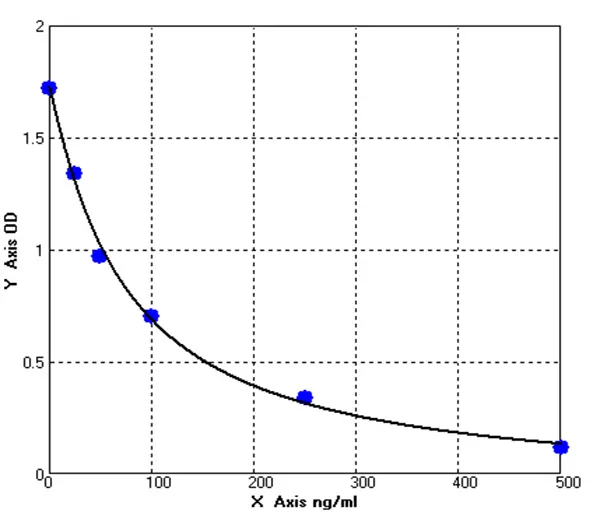
-
Canine Galectin 3 ELISA kit (E08G0052)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08G0052
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
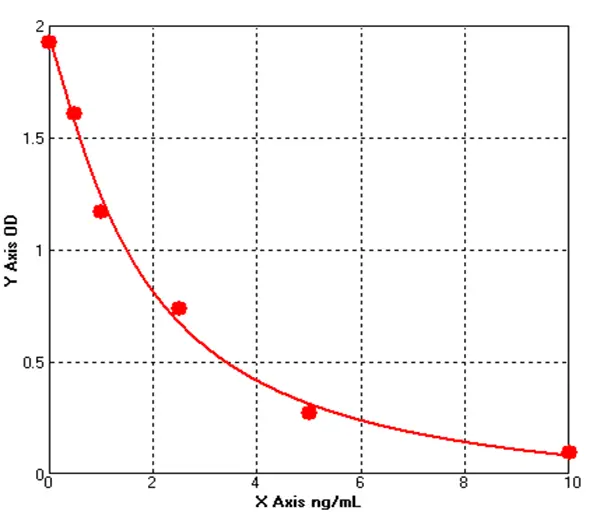
-
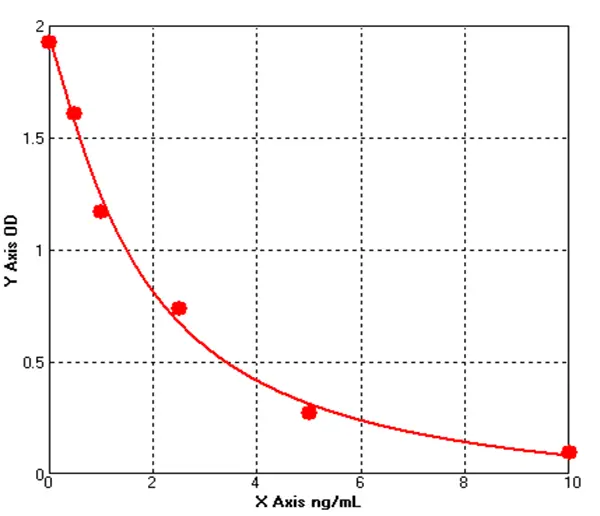
Canine Endothelin 1 ELISA kit (E08E0040)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08E0040
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
-
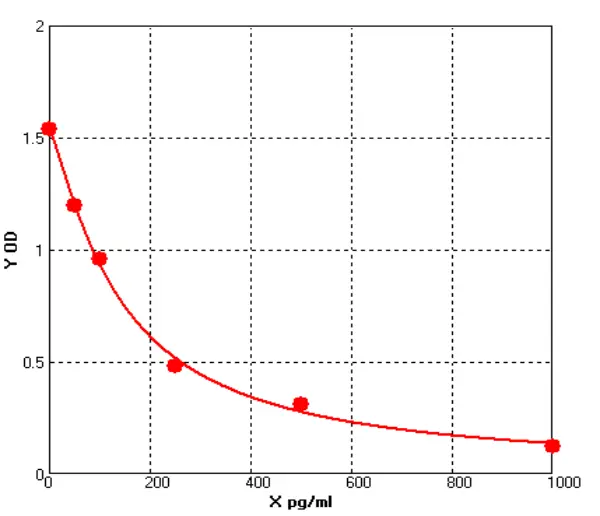
Canine Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases 1 ELISA kit (E08T0047)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08T0047
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml
-
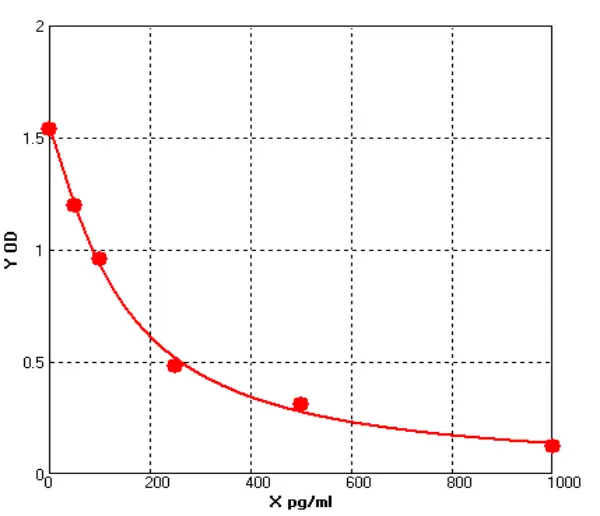
Canine Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha ELISA kit (E08T0008)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08T0008
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml
-
Canine Interferon β ELISA kit (E08I0344)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08I0344
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml

-
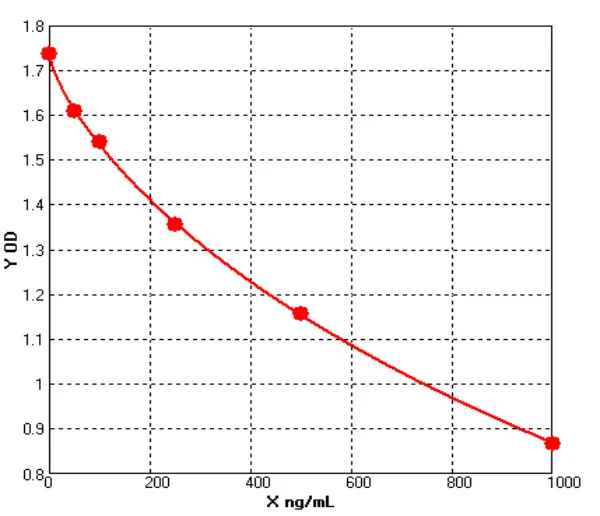
Canine Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor ELISA kit (E08V0010)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08V0010
Detection Range: 50-1000ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/ml
-
Canine Interleukin 6 ELISA kit (E08I0006)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08I0006
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml

-
Canine Melatonin ELISA kit (E08M0005)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08M0005
Detection Range: 50-1000pg/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml

-
Canine Myeloperoxidase ELISA kit (E08M0032)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08M0032
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/ml
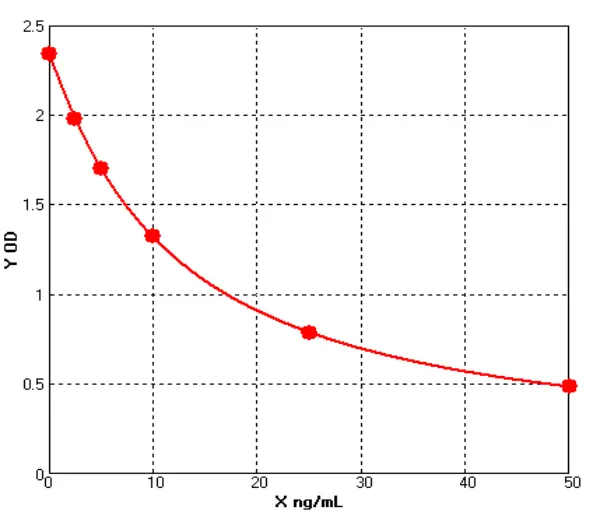
-
Canine Adenosine Monophosphate Activated Protein Knase α2 ELISA kit (E08P0188)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08P0188
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/mL
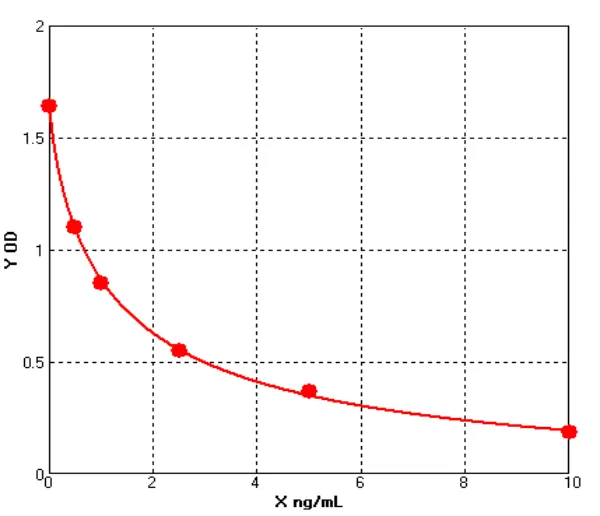
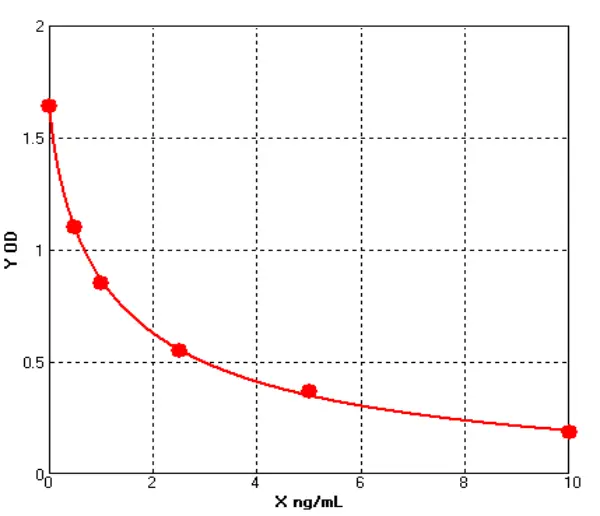
-
Canine Lipopolysaccharides/lipooligosaccharide ELISA kit (E08L0268)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08L0268
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/ml
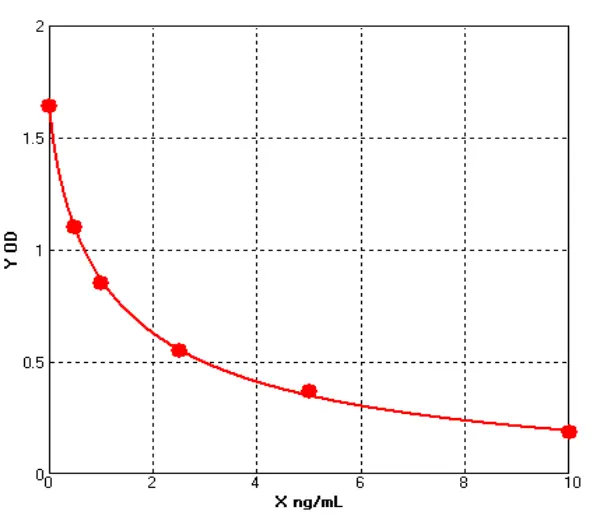
-
Canine Nerve Growth Factor ELISA kit (E08N0014)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08N0014
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/ml
-
Canine Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase gp91phox ELISA kit (E08N0010)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08N0010
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/ml

-
Canine Peptidoglycan ELISA kit (E08P0182)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08P0182
Detection Range: 0.5-10ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/ml

-
Canine Matrix Metalloproteinase 8 ELISA kit (E08M0325)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08M0325
Detection Range: 1.0-25ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/ml

-
Canine Prostaglandin E2 ELISA kit (E08P0012)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08P0012
Detection Range: 2.5-50ng/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 0.1ng/ml
-
Canine Hyaluronan synthase 1 ELISA Kit (E08H1411)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08H1411
Detection Range: 25-500ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/ml
-
Canine Hyaluronan synthase 2 ELISA Kit (E08H1412)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08H1411
Detection Range: 25-500ng/ml
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0ng/ml

-
Canine Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide ELISA kit (E08G0177)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08G0177
Detection Range: 250-5000pg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml
-
Canine Neuron Specific Enolase ELISA kit (E08N0025)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08N0025
Detection Range: 250-5000pg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml

-
Canine Neuropeptide Y ELISA kit (E08N0025)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08N0009
Detection Range: 250-5000pg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml

-
Canine Neurotrophin 3 ELISA kit (E08N0018)MANUAL
Cat. No.: E08N0018
Detection Range: 250-5000pg/mL
Reactivity: Canine
Sensitivity: 1.0pg/ml

Canine ELISA Kits FAQs
-
Q
What kinds of canines are normally used in the research, and what is the scope of application?
Experimental canines have wide usage. Experimental surgery is widely used in all aspects of experimental surgery, such as cardiovascular surgery, brain surgery, limb replantation, organ or tissue transplantation, etc. The medical experimental research canines are one of the most commonly used animals in basic medical research and teaching, especially in physiological, pharmacological, pathophysiological and other experimental studies. For chronic experimental research, due to canines' well cooperation with experiments through short-term training, they are very suitable for chronic experiments, such as conditioned reflex experiment, observation of therapeutic effect of various experiments, toxicology experiment, endocrine gland removal experiment, etc. About Pharmacological toxicological research and drug metabolism research, there are researches like the study on metabolism of sulfonamides and as well as the toxicity test of various new drugs before clinical use. Common experimental canines include beagles, 4-way hybrid canines, Mexican hairless canines and domestic canines (such as Chinese hounds, Tibetan shepherd canines, wolf canines, four eyed canines, North China canines, and northwest canines).
-
Q
How to determine whether the sample concentration is within the normal range?
The distribution of samples has normal and skewed types, and the appropriate statistical method should be selected according to the different types of data distribution. The basic statistical principles include the percentile method, normal distribution method, non-parametric method, geometric mean method, etc. For a large number of samples, not less than 100 cases, the closer the sample distribution is to the overall distribution, the more reliable the results will be, and the result is likely to get closer to the normal range. For overall samples, the quality requirements must be met. it is necessary to exclude extreme data and exclude the gender and age factors of the sample. In addition, the instrument reagents used, operating proficiency, method accuracy, and records must be unified, and try to be consistent with the actual situation.