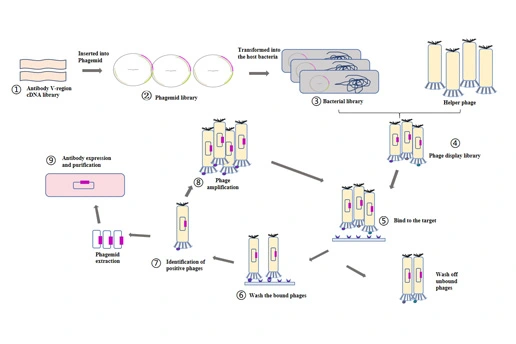
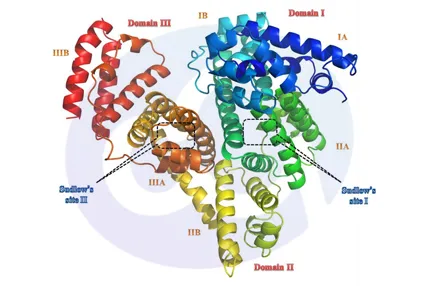
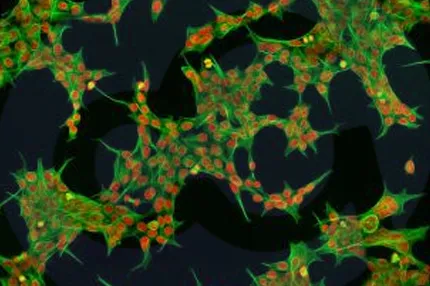
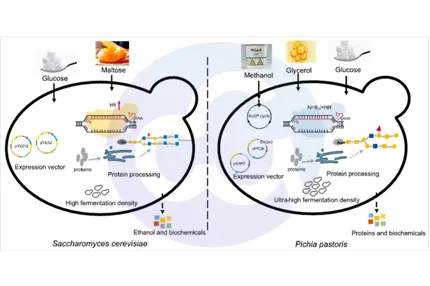
-
Host Cell Protein Detection Kits
- CHO Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- E. coli Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- HEK 293 Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- Pichia pastoris Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- Ogataea polymorpha Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit, G3
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit, G3
- Spodoptera fugiperda 9 (Sf9) Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit, G3 (Applicable to Sf9 and related cell lines)
- Dilution Buffer
-
Bioprocess lmpurity ELISA Kits
- Human Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA Kit
- Goat Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA Kit
- Human Serum Albumin (HSA) ELISA Kit
- NE01I0004 Human Insulin (INS) ELISA Kit ( Double Antibody Sandwich Method )
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) ELISA Kit
- Dextran Sulfate Salt Detection Kit (Spectrophotometric Method-200 Tests)
- Protein L (PL) ELISA Kit
- Kanamycin (KA) ELISA Kit
- Human Immunoglobulin A (IgA) ELISA Kit
- Human Immunoglobulin M (IgM) ELISA Kit
- Mouse Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA kit
- Bovine Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA kit
- Protein A (PA) ELISA kit-Boiling
- Protein A (PA) ELISA Kit
- Diluent Buffer for Protein L ELISA kit
-
Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kits
- CHO HCD Residue Detection Kits
- NS0 HCD Residue Detection Kits
- Vero HCD Residue Detection Kits
- E.coli HCD Residue Detection Kits
- HEK293 HCD Residue Detection Kits
- PP HCD Residue Detection Kits
- MDCK Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kit
- Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kit
- Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kit_copy20260304112530
- Ogataea polymorpha Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kit
- Magnetic Residual DNA Sample Preparation Kit
- DNA Dilution Buffer
- Residual Total RNA Detection Kits (qRT-PCR)
- Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
- ELISA Kits
- Cellular Component Protein Library
- Plasmids
- Promotions
-
BSA: Familiar Yet Unfamiliar – Launch of the Anti-Interference BSA ELISA Kit
Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) is widely used in in vitro diagnostics and the industrial production of biopharmaceuticals, making it a familiar name in the field. However, its source, structure, function,...
Feb.24, 2026Read More > -
HEK293 HCP ELISA: Fit for Viral Purification Processes, That’s What Truly Matters
Origin of HEK 293Human Embryonic Kidney 293 cells, commonly referred to as HEK 293, HEK-293, or 293 cells, are an immortalized cell line isolated from the embryo of a pregnant female in the 1970s[1].I...
Feb.11, 2026Read More > -
Yeast Family: Pichia pastoris (GS115) HCP ELISA
1. Application Background:Pichia pastoris is one of the most widely used expression systems for innovative antibody expression in vaccines nowadays. Yeast is extensively applied in modern industry [1]...
Jan.20, 2026Read More >
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology focuses on clarifying the essence of life. It mainly studies the structure and function of biological macromolecular nucleic acids and proteins and the transmission and regulation of life information. The main research contents include the molecular biology of nucleic acid, molecular biology of protein and molecular biology of cell signal transduction.
Molecular biology has developed rapidly since the middle of the 20th century. One of the most important reasons is the progress of gene operation and gene engineering technology. Basic operations include: cutting and joining of DNA, nucleic acid hybridization, gel electrophoresis, cell transformation, nucleic acid sequence analysis, artificial gene synthesis, site-directed mutagenesis and PCR amplification. This is the core technology of molecular biology research. Genetic engineering refers to inserting nucleic acid molecules into vector molecules in vitro to make them enter host cells for continuous and stable reproduction and expression. The ability to cross the barrier of natural species and place genes from any organism in new host biological cells without kinship is the fundamental feature that distinguishes genetic engineering technology from other technologies.