Search ELISA Kits
TGF-β Family Proteins Types
-
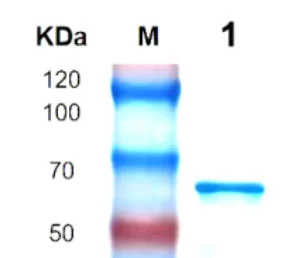
P01T0004 Human Transforming Growth Factor β2 (TGFB2) Protein, RecombinantMANUAL
Cat. No.: P01T0004
Uniprot No.: P61812
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression region: 1-442aa
Fusion Tag: 6×His-SUMO (N-terminus)
-
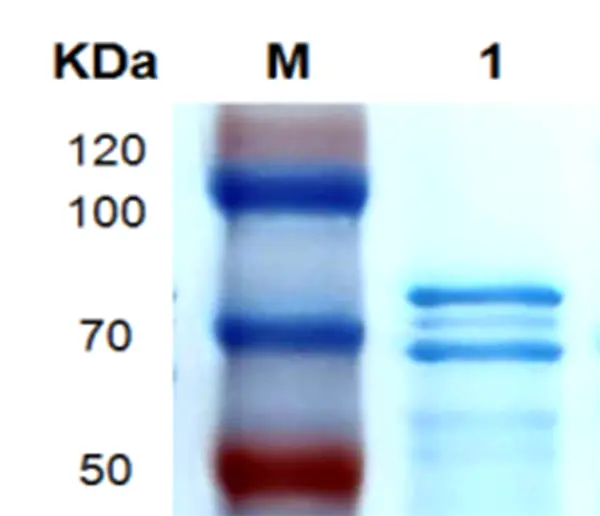
P01T0005 Human Transforming Growth Factor β3(TGFB3) Protein, RecombinantMANUAL
Cat. No.: P01T0005
Uniprot No.: P10600
Expression Host: E.coli
Expression region: 1-412aa
Fusion Tag: 6×His-SUMO (N-terminus)
TGF-β Family Proteins FAQs
-
Q
Differentiation plasticity regulated by TGF-β family proteins in development and disease
The biological function of TGF-β includes inflammation, tissue repair and embryonic development. Generally speaking, TGF-β has the effects of stimulating cells of mesenchymal origin and inhibiting cells of epithelial or neuroectodermal origin. For example, it can inhibit the proliferation of immunocompetent cells, regulate cell phenotype, and inhibit the differentiation of lymphocytes and the production of cytokines. It can promote the growth of fibroblasts, osteoblasts and Schwann cells, and inhibit the growth of epithelial cells, osteoclasts, endothelial cells and the formation of fat, myocardium and skeletal muscle. TGF-β can antagonize some biological functions of EGF. TGF-β has potential application prospects in treating wound healing, promoting cartilage and bone repair, and treating autoimmune diseases and transplantation rejection through immunosuppression.
-
Q
What is TGF beta?
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) belongs to a group of newly discovered superfamily TGF-β regulating cell growth and differentiation. It can combine with the corresponding receptors on the cell surface to change the phenotype of normal fibroblasts, that is, under the condition that epidermal growth factor (EGF) exists at the same time, it can change the adherent growth characteristics of fibroblasts to obtain the ability to grow in agar, and lose the density-dependent inhibition of growth.