-
Host Cell Protein Detection Kits
- CHO Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- E. coli Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- HEK 293 Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- Pichia pastoris Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit
- Ogataea polymorpha Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit, G3
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit, G3
- Spodoptera fugiperda 9 (Sf9) Host Cell Protein ELISA Kit, G3 (Applicable to Sf9 and related cell lines)
- Dilution Buffer
-
Bioprocess lmpurity ELISA Kits
- Human Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA Kit
- Goat Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA Kit
- Human Serum Albumin (HSA) ELISA Kit
- NE01I0004 Human Insulin (INS) ELISA Kit ( Double Antibody Sandwich Method )
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) ELISA Kit
- Dextran Sulfate Salt Detection Kit (Spectrophotometric Method-200 Tests)
- Protein L (PL) ELISA Kit
- Kanamycin (KA) ELISA Kit
- Human Immunoglobulin A (IgA) ELISA Kit
- Human Immunoglobulin M (IgM) ELISA Kit
- Mouse Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA kit
- Bovine Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA kit
- Protein A (PA) ELISA kit-Boiling
- Protein A (PA) ELISA Kit
- Diluent Buffer for Protein L ELISA kit
-
Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kits
- CHO HCD Residue Detection Kits
- NS0 HCD Residue Detection Kits
- Vero HCD Residue Detection Kits
- E.coli HCD Residue Detection Kits
- HEK293 HCD Residue Detection Kits
- PP HCD Residue Detection Kits
- MDCK Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kit
- Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Host Cell DNA Residue Detection Kit
- Magnetic Residual DNA Sample Preparation Kit
- DNA Dilution Buffer
- Residual Total RNA Detection Kits (qRT-PCR)
- Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
- ELISA Kits
- Cellular Component Protein Library
- Plasmids
- Promotions
-
HEK293 HCP ELISA: Fit for Viral Purification Processes, That’s What Truly Matters
Origin of HEK 293Human Embryonic Kidney 293 cells, commonly referred to as HEK 293, HEK-293, or 293 cells, are an immortalized cell line isolated from the embryo of a pregnant female in the 1970s[1].I...
Feb.11, 2026Read More > -
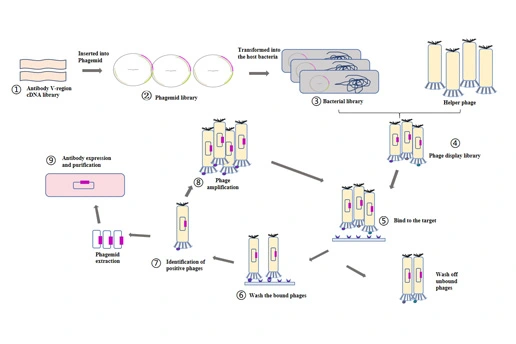
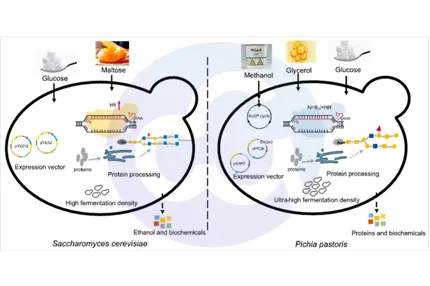
Yeast Family: Pichia pastoris (GS115) HCP ELISA
1. Application Background:Pichia pastoris is one of the most widely used expression systems for innovative antibody expression in vaccines nowadays. Yeast is extensively applied in modern industry [1]...
Jan.20, 2026Read More > -
Authoritative Certification
Recently, Cellgene Bioscience Co., Ltd. attained another notable achievement. In the Laboratory Proficiency Testing Program for Residual Vero Cell Protein Quantification in Vaccines (Program No.: NIFD...
Dec.23, 2025Read More >
Cytobiology
At different levels (microscopic, ultramicroscopic and molecular levels), it mainly studies cell structure and function, cell proliferation, differentiation, ageing and apoptosis, cell signal transduction, eukaryotic gene expression and regulation, cell origin and evolution. The main contents of its research include the study of the nucleus, chromosome and gene expression, the study of biofilm and organelles, the study of cytoskeleton system, cell proliferation and its regulation, cell differentiation and its regulation, cell ageing and apoptosis, cell origin and evolution, and cell engineering.
The cell is the basic unit of the organization and function of an organism and the basic unit of life activities. All organisms from single cells to higher animals and plants are composed of cells. Cells are the basic unit of all animals and plants, and all cells come from existing cells. Cell biology is a science that uses modern technology and methods to study the basic rule of cell life activities from different levels such as cells, ultrastructure and molecules. Medical cell biology is a subject based on cell biology and molecular biology to explore and study the relationship between human cell genesis, development, appreciation, ageing, death, abnormal cell structure and function and human diseases. Molecular cell biology is a subject that mainly studies the structure and function of cells and the laws of various life activities at the molecular level. It represents the mainstream and level of the development of modern cell biology and is the latest stage of the development of cell biology.