Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can also be called CSF2.
Specifications Of P01G0016E-T3 Human Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) Protein, Recombinant
| Product Information | |
catalog number | P01G0016E-T3 |
Package Size | 10ug/50ug/500ug/1mg |
Other Names | CSF2 |
Protein & NCBI Number | M11220, P04141 |
Host | 293T |
Express Region | Ala18-Glu144 |
Protein Sequence | APARSPSPSTQPWEHVNAIQEARRLLNLSRDTAAEMNETVEVISEMFDLQEPTC |
Molecular Weight | The protein consists of 161 amino acids (including the fusion tag), with a predicted molecular weight of |
Fusion Tag | 6×His (C-terminus) |
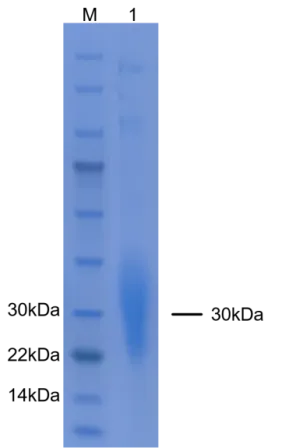
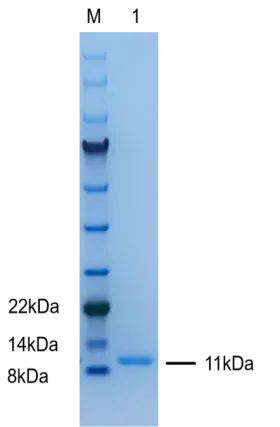
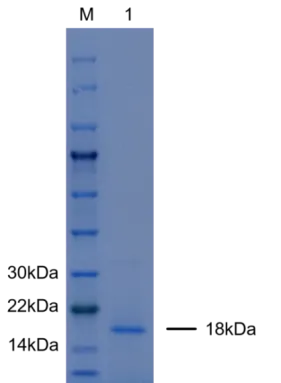
Purity | ≥95% SDS-PAGE |
Physical Property | Liquid |
Components | 0.01M PBS+20% glycerol, sterile solution. |
Storage & Stability | After aliquoting, the stability of the samples can be maintained for up to 6 months at |
Applications | Antibody preparation, immunoassay (ELISA, WB), subcellular localization and |
Lead Time | 5 to 10 business days; 2 to 3 days for stock products |
Background |
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF), also known as Colony-Stimulating Factor 2 (CSF2), is a monomeric glycoprotein. Unlike Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF), which specifically promotes the proliferation and maturation of neutrophils, GM-CSF affects a broader range of cell types, particularly macrophages and eosinophils. High levels of GM-CSF have been detected in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and targeting GM-CSF as a biological target can reduce inflammation or tissue damage. In critically ill patients, GM-CSF has been trialed as an immunosuppressive therapy, showing potential in restoring the function of monocytes and neutrophils. The functions of GM-CSF include: Hematopoiesis and differentiation of bone marrow lineage cells; Development and maintenance of alveolar macrophages; Recruitment and differentiation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs), including the production of IL-23 and polarization of TH17 T cells; Maturation and antigen presentation by conventional DCs, such as CD103-expressing DCs in the skin and small intestine; Polarization of M1 macrophages, including the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, phagocytosis, and antigen presentation; Priming and activation of neutrophils, including processes such as phagocytosis, oxidative bursts, and nitric oxide generation. |
Related Products Of Human Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) Protein, Recombinant
P01I0345P-T2 Human Interferon γ (IFNγ) Protein, Recombinant
P01R0005P-T2 Human Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) Protein, Recombinant
P01R0005P Human Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) Protein, Recombinant
P01G0016P-T2 Human Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) Protein, Recombinant
P01G0016E-T3 Human Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) Protein, Recombinant
P03G0016P-T2 Mouse Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) Protein, Recombinant
P03G0016E-T3 Mouse Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) Protein, Recombinant
P01S0011P Human Stem Cell Factor (SCF) Protein, Recombinant