Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) can also be called Pro-epidermal growth factor, EGF.
Specifications Of P01E0032P Human Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Protein,Recombinant
Product Information | |
Catalog Number | P01E0032P |
Package Size | 10ug/50ug/500ug/1mg |
Other Names | Pro-epidermal growth factor, EGF |
Protein & NCBI Number | NM_001963.6, P01133 |
Host | E.coli |
Express Region | Asn971-Arg1023 |
Protein Sequence | NSDSECPLSHDGYCLHDGVCMYIEALDKYACNCVVGYIGERCQYRDLKWWELR |
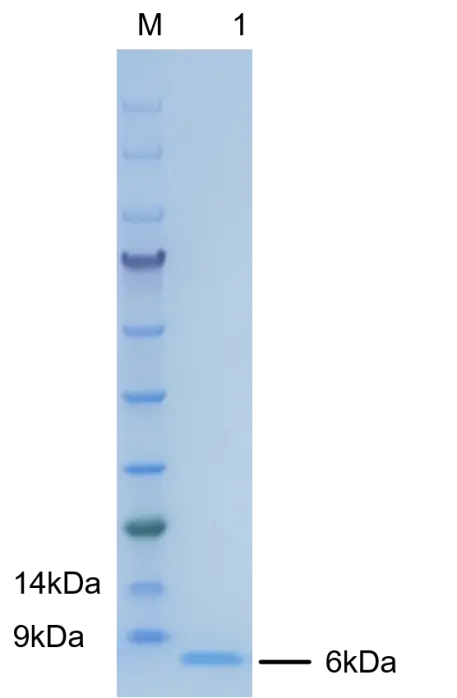
Molecular Weight | The protein consists of 53 amino acids (including the fusion tag), with a predicted molecular weight of 6.2kDa, which matches the actual molecular weight. |
Fusion Tag | None |
Purity | ≥95% SDS-PAGE |
| Physical Property | Liquid |
Components | 0.01M PBS+20% glycerol, sterile solution |
Storage & Stability | After aliquoting, the stability of the samples can be maintained for up to 6 months at -20°C to -80°C, |
Applications | Antibody preparation, immunoassay (ELISA, WB), subcellular localization, |
Lead Time | 5 to 10 business days 2 to 3 days for stock products |
Background |
Human epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a 6-kDa protein with 53 amino acid residues and three intramolecular disulfide bonds. By binding to the homologous receptor EGFR on the cell surface, EGF can stimulate cell growth, differentiation, and survival. EGF stimulates the growth of various epidermal and epithelial tissues both in vivo and in vitro, and it also stimulates the growth of some fibroblasts in cell culture. This stimulation leads to ligand-induced dimerization, which activates the intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor. The tyrosine kinase activity, in turn, initiates a signaling cascade that results in a variety of biochemical changes within the cell: an increase in intracellular calcium levels, an increase in glycolysis and protein synthesis, an increase in the expression of certain genes (including the EGFR gene), and ultimately, DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. EGF was initially described as a secretory peptide found in mouse submandibular glands and human urine. Subsequently, EGF has been found in many human tissues and fluids, including platelets, urine, saliva, milk, tears, plasma, submandibular glands, and parotid glands. Initially, human EGF was referred to as urogastrone. |
Related Products Of Human Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Protein,Recombinant
P01F0003P Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Protein, Recombinant
P01F0003P-T2 Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Protein, Recombinant
P01I0420P-T2 Human Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Long R3 Analog (IGF1-LR3) Protein, Recombinant
P01V0016E-T3 Human Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165) Protein, Recombinant
P01F0073P-T2 Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 (FGF9) Protein, Recombinant
P01I0420P Human Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Long R3 Analog (IGF1-LR3) Protein, Recombinant
P01E0032P-T2 Human Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Protein, Recombinant
P01F0221P-T2 Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 (FGF10) Protein, Recombinant