E.coli Residual Total RNA Detection Kit (qRT-PCR)–Significance and Regulatory Context
Significance of E. coli Residual Total RNA Detection
Exogenous host cell nucleic acid contamination is a critical concern in biologics. DNA is the primary contaminant with potential theoretical risks (e.g., oncogenicity, infectivity), whereas RNA is considered low-risk, as it is rapidly degraded and cleared by endogenous RNases in the human body. Regulatory authorities including the FDA, EMA, and NMPA mandate explicit testing for host cell-derived impurities[1-5].
Several studies have reported the mechanisms by which the innate immune system recognizes DNA and RNA, primarily through both TLR-dependent and TLR-independent pathways. The core of RNA immunogenicity lies in how pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect exogenous nucleic acids and activate innate immune responses. PRRs are critical in controlling pathogen infection, particularly RNA virus infection.
Major RNA-sensing PRRs include TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, RIG-I, MDA5, NLRP3, NOD2, and a few others (Figure 1). Specifically, TLR7 and TLR8 recognize single-stranded RNA (ssRNA), while TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). RIG-I and MDA5 detect viral RNA in the cytoplasm—RIG-I recognizing short dsRNA with 5′-triphosphate ends, and MDA5 recognizing long dsRNA. As cytosolic sensors, RIG-I–like receptors serve as key sentinels of antiviral immunity[6].
In addition, RNA may also function in an mRNA-like manner, entering host cells, being translated, and presented on the cell surface[7] (Figure 2).
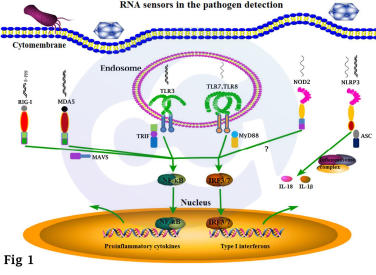

Figure 1 Figure 2
Regulatory Requirements
Endogenous mammalian RNA is typically modified (e.g., methylation) and compartmentalized within organelles, thereby shielding it from PRR recognition and preventing autoimmune activation. By contrast, bacterial and viral RNAs lack such modifications and are readily identified as “non-self.”
These exogenous RNAs bind to PRRs, which are typically activated within the endosomes of immune cells such as plasmacytoid dendritic cells and macrophages, leading to the production and release of type I interferons (IFN-α/β) and proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6). This may induce flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, headache, and myalgia.
Although massive systemic inflammation could theoretically cause cytokine storm and severe toxicity, such levels of exogenous RNA are highly unlikely in purified biologics. Nevertheless, prolonged or repeated immune activation might result in immunosuppression or exhaustion, but this would also require abnormally high exposure levels. For these reasons, regulatory agencies increasingly require process validation to ensure efficient clearance of such impurities.
Such strong, systemic inflammatory responses could theoretically trigger cytokine storms and severe toxicity; however, this would require exceptionally high levels of exogenous RNA, which are highly unlikely in purified biologics.
In specific scenarios, persistent or repeated immune activation may eventually lead to immunosuppression or exhaustion, yet this also demands extreme exposure levels.
Therefore, regulatory agencies increasingly emphasize validation of impurity clearance processes. Efficient removal of DNA and host cell proteins (HCPs) to acceptable levels is systematically controlled.
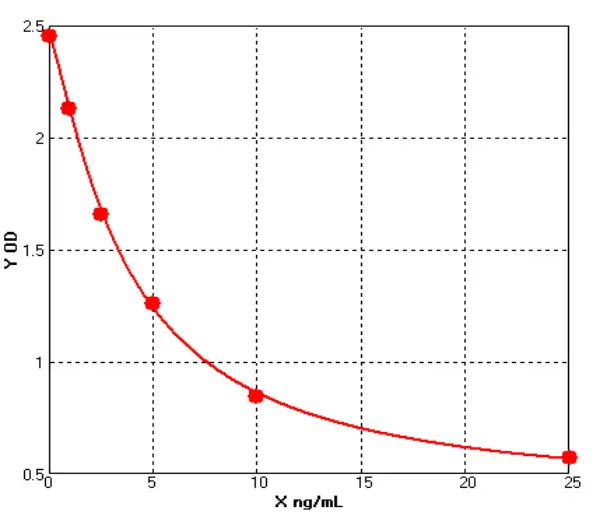
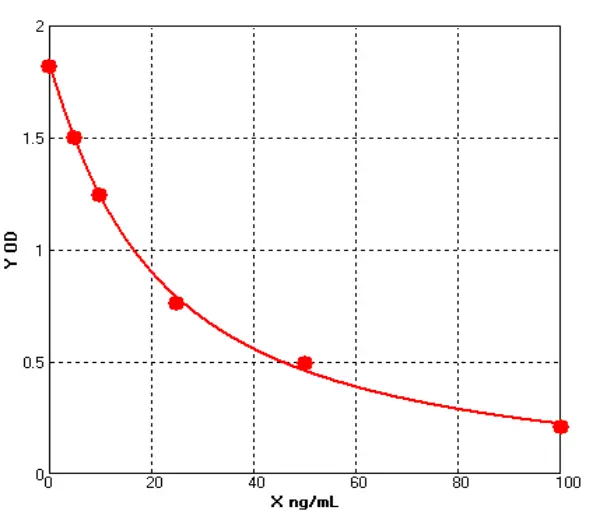
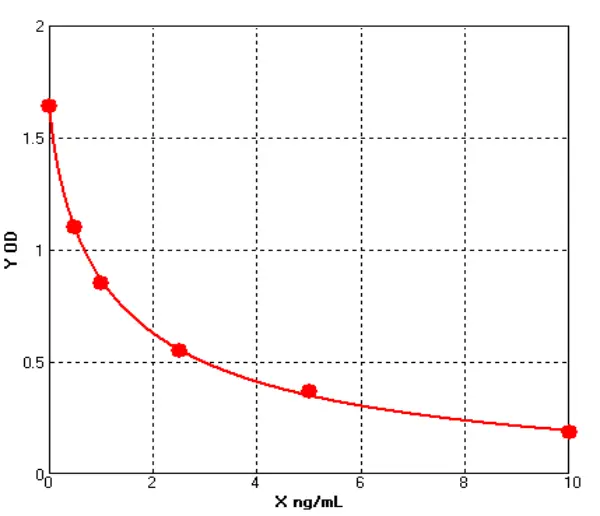
In line with current and emerging regulatory expectations, Cellgene Bioscience has developed a comprehensive portfolio of E. coli–derived host cell impurity detection kits—including protein, DNA, and RNA (Table 1, Figures 3, Tables 2, Table 3)—aiming to provide robust and reliable quality control for biologics.
Table 1
| Source | Product Name | Catalog No. | Detection Range |
| Host Cell Protein (HCP) | E.coli HCP (3S) | EH-E0020-1 | 0-250ng/mL |
| E.coli HCP (6S) | EH-E0022-3 | 0-250ng/mL | |
| Host Cell DNA (HCD) | E.coli HCD | EC-D050T/EC-D100T | 0.03-300pg/uL |
| Host Cell RNA | E.coli Total RNA (qRT-PCR) | EC-R100T | 0.002-20pg/uL |
| Supporting Kits/Buffers | Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit (QPCR) | CG-DP100 | / |
| HCP Diluent Buffer (ELISA) | CH-DIL1 | / |
Data:
Figure 3
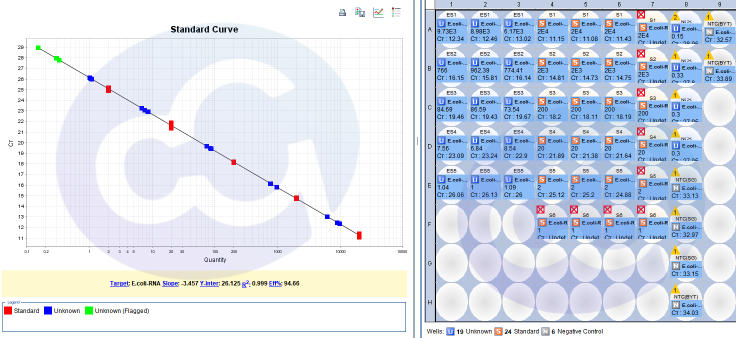
Table 2
QC | E.coli Residual Total RNA Detection Kit (qRT-PCR) |
STD Curve | 0.002-20pg/uL,R²>0.99 |
Linear | 50%-150% |
Recovery | 50%-150% |
Amplification Efficiency (%) | 90%≤Eff%≤110%, |
Slope | -3.8~-3.1 |
Table 3
Compatible Instrument(s) | ROX Reference Dye |
ABI PRISM 7000/7300/7700/7900HT/7900HT Fast,ABI Step One, ABI Step One Plus | ROX Reference Dye(50X) |
ABI 7500/7500Fast Stratagene Mx3000P/Mx3005P/Mx4000 MJ Research Chromo4, Opticon (II), Corbett Rotor Gene 3000 | ROX Reference DyeⅡ(50X) |
Roche/Bio-Rad/Eppendorf instrument, etc. | No ROX |
Reference:
[1] ICH Q6B:Specifications: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for Biotechnological/Biological Products.
[2] ICH Q7:Good Manufacturing Practice Guide for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients.
[3] USP:<1130> Nucleic Acid-Based Techniques; <508> Residual Host Cell Protein Measurement
[4] EP:2.6.7. Nucleic acid amplification techniques ; 5.2.3. Cell substrates for the production of vaccines for human use.
[5] ChP:《生物制品生产用原材料及辅料质量控制》、《人用重组DNA蛋白制品总论》
[6] Nanhua Chen, et al. RNA sensors of the innate immune system and their detection of pathogens. IUBMB Life. 2017. 69(5):297-304.
[7] Abishek Wadhwa, et al. Opportunities and Challenges in the Delivery of mRNA-based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics. 2020. 12(2):102.
Cellgene Bioscience has been dedicated to the biopharmaceutical and industrial testing field for 15 years, offering a series of HCP residual detection products, as well as comprehensive technical services including HCP-specific antibody development and coverage analysis.
https://www.elisakit.cc/
Cellgene Bioscience-Drug Residue Detection Products | |
Host Cell Protein ELISA kits (HCP) | |
CH-K0018-2 | CHO Host Cell Protein (CHO HCP) ELISA kit, G2 |
CH-K0018-3 | CHO Host Cell Protein (CHO HCP) ELISA kit, G3 |
HH-H0019-2 | HEK293 Host Cell Protein (HEK293 HCP) ELISA kit, G2 |
EH-E0020-3 | E. coli Host Cell Protein (E. coli HCP) ELISA kit, G3 |
PH-E0021-3 | Pichia pastoris Host Cell Protein (PP HCP) ELISA kit, G3 |
HP-H0023-3 | Ogataea polymorpha Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
SC-H0024-3 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
SF-H0025-3 | Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
Medium Residues Detection kits | |
NEGES0890 | Protein A ELISA Kit (Boiling) |
NEGEP0890 | Protein A ELISA Kit |
NE03I0431 | Mouse Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit |
NE11I0431 | Bovine Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit |
NE01I0431 | Human Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit |
NE06I0431 | Goat Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit |
NEGEK0006 | Kanamycin ELISA Kit |
NEGEP1270 | Protein L ELISA Kit |
NEGEP1271 | Protein G ELISA Kit |
NEGES0014 | Bovine Serum Albumin ELISA Kit |
NEGES0015 | Human Serum Albumin ELISA Kit |
NEGED0018 | Dextran Sulfate Salt Detection kit |
Host Cell DNA Detection kits (HCD) | |
NS-D050T/NS-D100T | NS0 Host Cell DNA (NS0 HCD) Residue Detection kit |
EC-D050T/EC-D100T | E.coli Host Cell DNA (E.coli HCD) Residue Detection kit |
VE-D050T/VE-D100T | Vero Host Cell DNA (Vero HCD) Residue Detection kit |
HK-D050T/HK-D100T | HEK293 Host Cell DNA (HEK293 HCD) Residue Detection kit |
CH-D050T/CH-D100T | CHO Host Cell DNA (CHO HCD) Residue Detection Kit |
PP-D050T/PP-D100T | Pichia Pastoris Host Cell DNA (PP HCD) Residue Detection Kit |
CG-DP050/CG-DP100 | Magnetic Residual DNA Sample Preparation Kit |
Residual Total RNA Detection Kit | |
EC-R100T | E.coli Residual Total RNA Detection Kit (qRT-PCR) |
Host Cell Protein Antibodies | |
CH-K0018-3-Ab | CHO Host Cell Protein G3 Antibody |
CH-K0018-2-Ab | CHO Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody |
EH-E0020-3-Ab | E.coli Host Cell Protein G3 Antibody |
PH-E0021-2-Ab | Pichia Yeast Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody |
HH-H0019-2-Ab | HEK293 Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody |
Buffer Products | |
CG-H0100 | HCP ELISA buffer |
CG-P0200 | Protein L ELISA buffer |