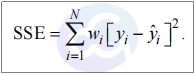HCP ELISA Development: The Path to Background Optimization
1. Background
1.1. Introduction to ELISA:
The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a highly sensitive and specific immunoassay technique based on the formation of antibody-antigen-antibody sandwich complexes. With its long-established history, mature technology, simple operation, cost-effectiveness, and high-throughput capability, ELISA has been widely applied in medicine (medical devices and precision instruments), biology, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and food safety. Depending on application requirements, ELISA can be classified into direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive methods.
1.2. Key applications of ELISA include:
Qualitative detection of viruses/bacteria/parasites
Quantitative measurement of protein antigens
Qualitative and quantitative studies of antibody titers and signaling pathways
Drug development and quality control, including quantification of drugs in blood/tissue fluids
Potency testing of biologics
1.3. Distinctive features of ELISA:
Precise antigen quantification via standard curves
Qualitative screening for target antigens
High-throughput analysis of large sample volumes
High sensitivity with detection limits reaching ng/mL to pg/mL
Specific antigen-antibody affinity interactions
1.4. Standard curves serve as the fundamental basis for quantification:
Core reference for quantification: Mathematical models are fitted using known standard concentrations and corresponding signals to calculate sample concentrations
Validation of assay reliability through:
Limit of Detection (LOD)
Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
Linear Range
Repeatability
Quality control: Slope and intercept values assess assay consistency, while data standardization minimizes inter-batch variability
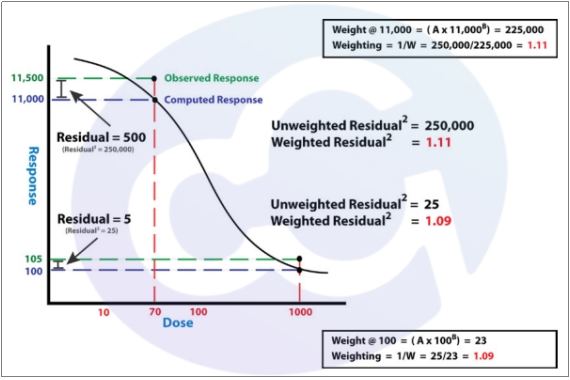
1.5. Sum of Squares Error (SSE) is crucial for evaluating:
1) Evaluation of Standard Curve Fitting Quality: Measures deviations between observed data points and predicted values.A smaller SSE indicates better agreement between the experimental data points and the fitted curve, reflecting higher fitting accuracy. An excessively large SSE suggests that the selected mathematical model may be inappropriate for the current experiment.
2) Assessment of Experimental Reliability: Comparable SSE values across standard curves (combined with R²) confirm experimental repeatability and reliability
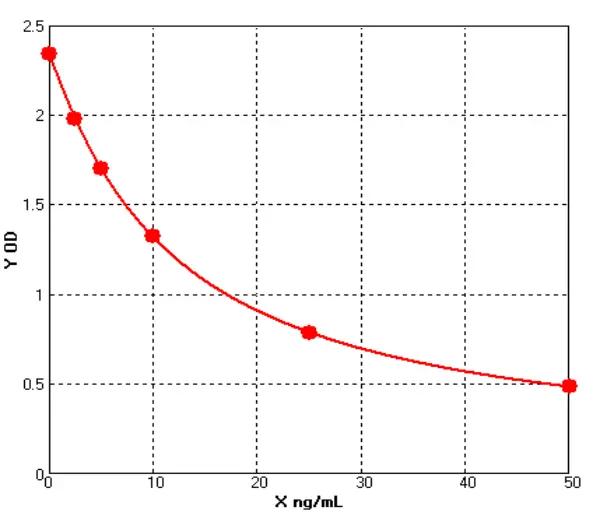
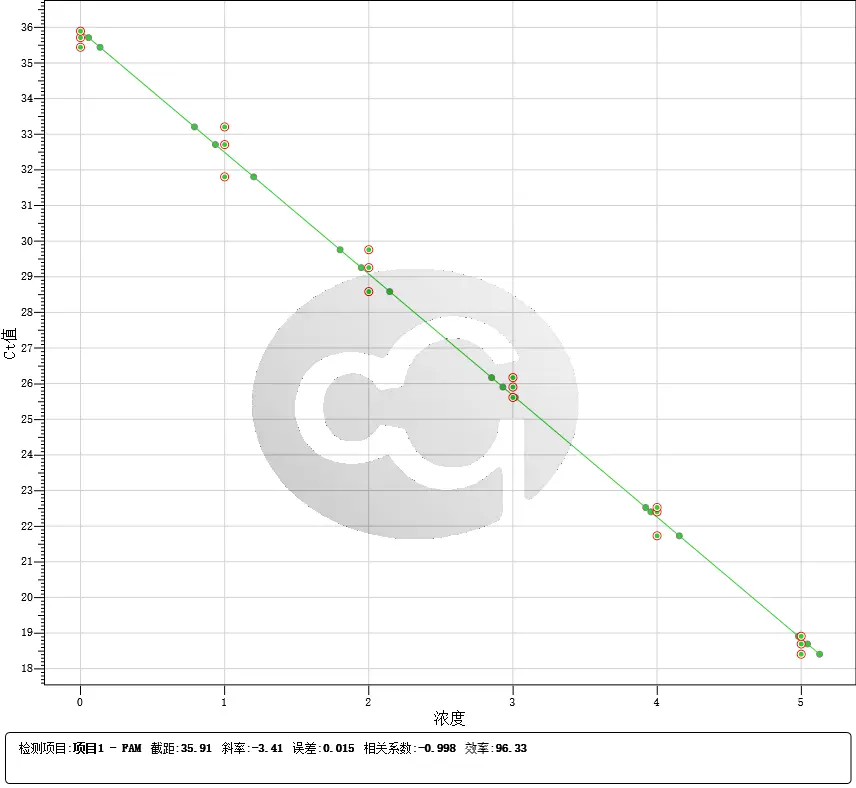
 |
|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
2. Role of ELISA Blank Controls
2.1. The blank wells critically impact assay performance in multiple ways:
SSE Calculation Impact: Crrected OD = Measured OD - Blank OD; Unstable or abnormal blank OD values increase data deviation after correction, elevating SSE and reducing fitting accuracy
Significant variation between blank wells indicates systematic experimental error
High blank signals may cause negative values for low-concentration standards, distorting the standard curve and increasing SSE
2.2. Regulatory Requirements
Key guidelines including:
Technical Review Guidelines for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Detection Reagent Registration
Guidelines for Analytical Performance Evaluation of Quantitative Detection Reagents
EP17-A2
Immunoassay Devices Guidance for Industry
Mandate the following blank control specifications:
Blank wells must be included in all quantitative ELISA experiments
Blank signal should be significantly lower than the lowest calibrator (typically Blank OD ≤ 50% of lowest calibrator OD)
Alternative criterion when used for LOD determination: Mean blank OD + 2SD ≤ low-concentration calibrator OD
For TMB substrates: OD450 ≤ 0.1
Blank well repeatability requirement: CV ≤ 20%
3. Practical Application
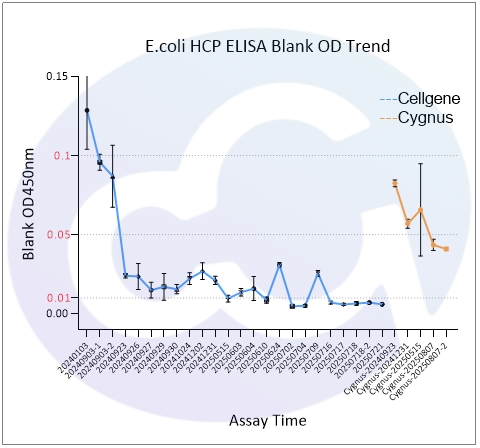
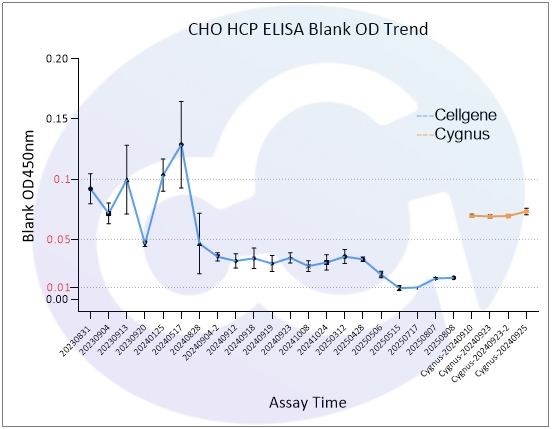
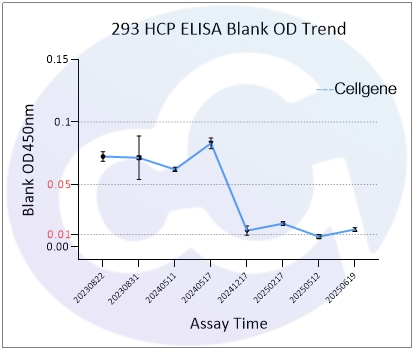
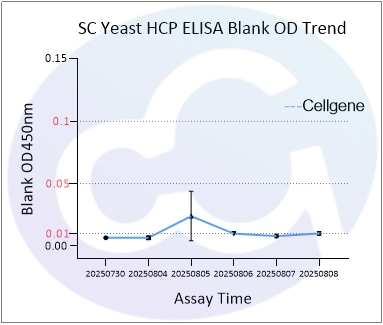
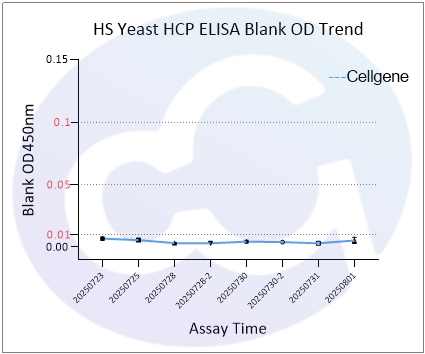
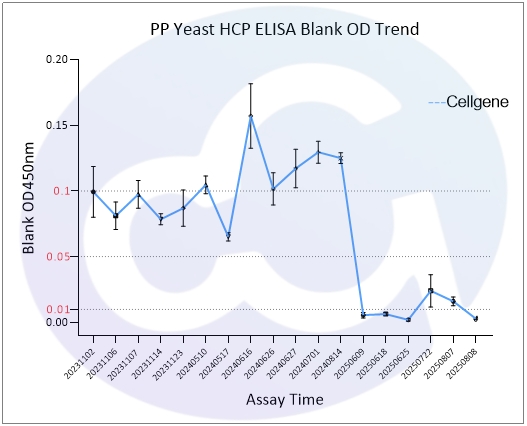
As all immunoassays require standardization, blank control represents a critical measure of ELISA quality. Through three years of dedicated development for E.coli/CHO/293/SC Yeast/HS Yeast/PP Yeast HCP ELISA kits, Cellgene Bioscience has achieved:
10-fold reduction in background levels
Documented progression from 0.1 to 0.05 to 0.01 OD levels
2-10 times lower background compared to Cygnus
These advancements (See Figure 1 and Figure 10) provide a robust foundation for accurate drug quantification in ELISA applications.
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
Figure 6 |
Figure 7 |
Figure 8 |
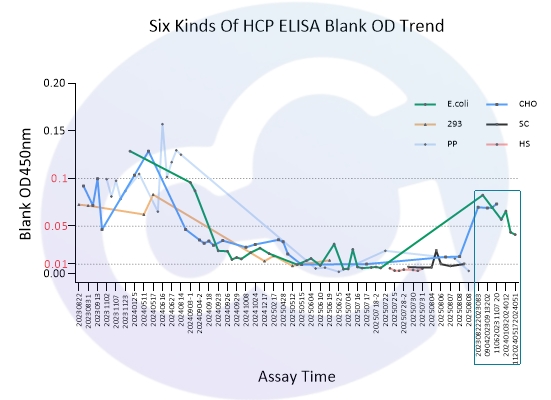
Figure 9
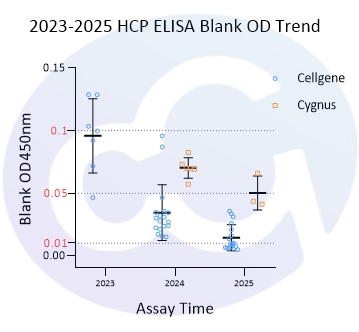
Figure 10
2023 | 2024 | 2025 | |
E.coli | 0.104 | 0.021 | 0.011 |
CHO | 0.090 | 0.034 | 0.021 |
293 | 0.072 | 0.053 | 0.014 |
SC | 0.011 | ||
PP | 0.089 | 0.111 | 0.009 |
HS | 0.004 | ||
Cygnus-E.coli | 0.07 | ||
Cygnus-CHO | 0.07 | 0.05 |
4. References:
Technical Review Guidelines for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Detection Reagent Registration
Guidelines for Analytical Performance Evaluation of Quantitative Detection Reagents
EP17-A2: Evaluation of Detection Capability for Clinical Laboratory Measurement Procedures; Approved Guideline—Second Edition
Immunoassay Devices Guidance for Industry
Cellgene Bioscience has spent 15 years dedicated to R&D in biopharmaceutical industrial testing. We offer a comprehensive HCP residual-detection product line and provide end-to-end technical services, including HCP-specific antibody generation and coverage analysis.
BlueGene Biotech: Elisa Kits, Recombinant Proteins, Plasmids & Other Reagents
Cellgene Bioscience-Drug Residue Products | |
Host Cell Protein ELISA kits (HCP) | |
CHO Host Cell Protein (CHO HCP) ELISA kit, G2 | |
CHO Host Cell Protein (CHO HCP) ELISA kit, G3 | |
HEK293 Host Cell Protein (HEK293 HCP) ELISA kit, G2 | |
E. coli Host Cell Protein (E. coli HCP) ELISA kit, G3 | |
Pichia Pastoris Host Cell Protein (PP HCP) ELISA kit, G3 | |
HP-H0023-3 | Hansenula Polymorpha Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
SC-H0024-3 | Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
SF-H0025-3 | Spodoptera Frugiperda 9 Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
Medium Residues Detection kits | |
Protein A ELISA Kit (Boiling) | |
Protein A ELISA Kit | |
Mouse Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Bovine Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Human Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Goat Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Kanamycin ELISA Kit | |
Protein L ELISA Kit | |
NEGEP1271 | Protein G ELISA Kit |
Bovine Serum Albumin ELISA Kit | |
Human Serum Albumin ELISA Kit | |
Dextran Sulfate Salt Detection kit | |
Host Cell DNA Detection kits (HCD) | |
NS0 Host Cell DNA (NS0 HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
E.coli Host Cell DNA (E.coli HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
Vero Host Cell DNA (Vero HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
HEK293 Host Cell DNA (HEK293 HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
CHO Host Cell DNA (CHO HCD) Residue Detection Kit | |
Pichia Pastoris Host Cell DNA (PP HCD) Residue Detection Kit | |
Magnetic Residual DNA Sample Preparation Kit | |
Host Cell Protein Antibodies | |
CHO Host Cell Protein G3 Antibody | |
CHO Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody | |
E.coli Host Cell Protein G3 Antibody | |
PH-E0021-2-Ab | Pichia Yeast Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody |
HEK293 Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody | |
Buffer Products | |
CG-H0100 | HCP ELISA buffer |
Protein L ELISA buffer | |