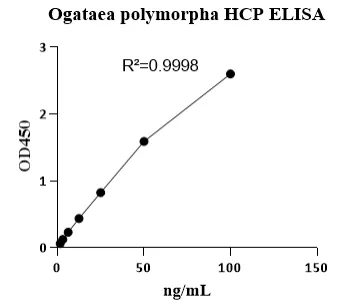
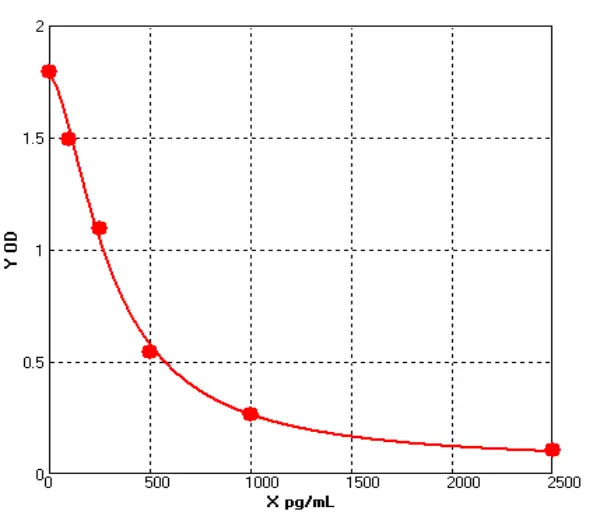
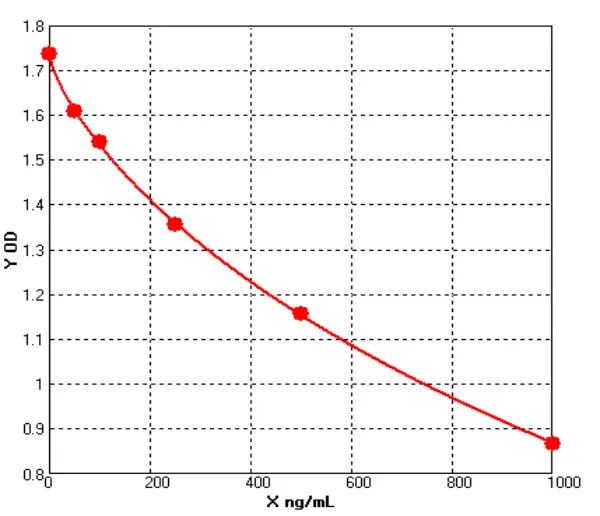
Performance Comparison of E.coli HCP ELISA Kits
Background:
Throughout the history of biopharmaceutical production, the effective removal and detection of HCP impurities in the final drug product has been a major focus of extensive research and discovery. The presence of these impurities can significantly impact drug stability and patient safety in clinical applications.
Currently, common protein drug expression systems include prokaryotic expression systems such as Escherichia coli (E.coli); plant expression systems; fungal systems such as Pichia pastoris and Saccharomyces cerevisiae; insect expression systems such as Spodoptera frugiperda cells (SF9); and mammalian expression systems such as Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and African green monkey kidney (Vero) cells. Among these, mammalian cell systems are more widely used in clinical drug production, although with high cost. In contrast, the E.coli expression system is the most widely used due to its high yield, low cost, and broad applicability.
The E.coli expression system is widely adopted across diverse application fields because of its simple cultivation, high transformation efficiency, low cost, and high yield. Proteins that do not require post-translational modifications—such as human insulin and growth hormone—as well as proteins that naturally require glycosylation but remain biologically active without it—such as α-, β-, and γ-interferons, interleukin-2, and tumor necrosis factor—can be successfully produced using E.coli[1,2].
HCP detection and identification are primarily conducted using ELISA and LC-MS, which are considered the gold standard methods. ELISA allows high-throughput quantification at a relatively low cost, while LC-MS provides both qualitative and quantitative analysis, but it is more expensive and has lower throughput. Therefore, both methods are often used in a complementary (orthogonal) manner for comprehensive HCP profiling.
Numerous studies have shown that even with identical purification processes, different drug—or the same drug with different manufacturing processes—can yield significantly varied HCP residue profiles. Consequently, HCP quantification results often differ across laboratories and geographies[3].
E.coli HCPs differ significantly from CHO HCPs and can be categorized into the following types:
Adhesins: Curli (CsgA), which form amyloid fibers and promote biofilm formation.
Toxins: α-hemolysin (HlyA), a pore-forming toxin that lyses red blood and epithelial cells.
Invasins: OmpA, which facilitate E.coli invasion through the blood-brain barrier (NMEC) and resist complement-mediated killing.
Immune evasion-related proteins: lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which induces inflammation while evading immune recognition.
Secretory system effector proteins: EspC, an autotransporter protease that disrupts epithelial barriers.
Host interaction effector proteins: NleH, which modulates host NF-κB signaling to reduce inflammation.
Phage/plasmid-encoded virulence proteins: Colibactin, a genotoxin that induces DNA damage.
Jones et al. reported that residual host cell proteins (HCPs) not only possess immunogenic potential but can also contribute to the degradation of pharmaceutical excipients. Therefore, strategies such as gene knockout of high-risk host-related factors or simulating the drug production and purification processes using null cell-derived HCPs are particularly important. These simulations—covering steps like depth filtration, affinity chromatography, and ion exchange chromatography—are essential for comprehensive analysis of HCP residuals. During process optimization, certain HCPs can be especially difficult to remove. Zhu et al. reported that, in the purification of a malaria vaccine expressed in E. coli, residual HCP levels ranged from 90 ng to <1100 ppm per dose. However, the clinically acceptable threshold for HCPs that do not lead to chronic conditions is typically <100 ppm[4,5,6].
Therefore, it is essential to conduct comprehensive HCP testing to avoid missed detections, while continuously improving assay sensitivity and coverage.
Cellgene Bioscience Product Performance:
Cellgene Bioscience’s newly developed E.coli HCP (6S) ELISA Kit (EH-E0022-3), which has been evaluated in comparison with Cygnus (USA) F410. The comparison was conducted across four parameters: standard curve range, relative sample variation, sample concentration detected, and background level.
Key advantages:
1. Lower background, enabling better exclusion of non-specific binding
2. More stable relative sample variation, with a broad detection range
3. Higher sample detection concentration. Please refer to Table 1 for detailed comparison data.
Standard Curve Range | Relative Sample Variation | Background Level (Fig.3) | Sample | Recovery Rate | |
| Cellgene | 0-250ng/mL | 7, -9% - 24% | 0.02 | 21.94μg/mL | 75% - 109% |
| Cygnus | 200ng/mL | 3, -27% - 24% | 0.08 | 13.65μg/mL | -0.78 |
Table 1


Figure 5
Reference:
[1] F. R.Schmidt. Recombinant expression systems in the pharmaceutical industry[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004. 65:363-372.
[2] Saskia R. et al. The production of biopharmaceuticals in plant systems[J]. Biotechnology Advances. 2009. 27(6):879-894.
[3] Chase E. Herman et al. Behavior of host-cell-protein-rich aggregates in antibody capture and polishing chromatography[J]. J Chromatogr A. 2023. 1702: 464081.
[4] Jones, M., et al. High-risk host cell proteins (HCPs): A multi-company collaborative view[J].Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2021. 118, 2870-2885
[5] Reiter, K., et al. Host cell protein quantification of an optimized purification method by mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2019. 174,650-654.
[6] Chiu, J., et al. Knockout of a difficult-to-remove CHO host cell protein, lipoprotein lipase, for improved polysorbate stability in monoclonalantibody formulations[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2017. 114, 1006-1015.
Cellgene Bioscience has been dedicated to the biopharmaceutical industry testing field for 15 years. We offer a comprehensive range of HCP residual detection products, as well as full-process technical services including HCP-specific antibody development and coverage analysis.
Cellgene Bioscience-Drug Residue Products | |
Host Cell Protein ELISA kits (HCP) | |
CHO Host Cell Protein (CHO HCP) ELISA kit, G2 | |
CHO Host Cell Protein (CHO HCP) ELISA kit, G3 | |
HEK293 Host Cell Protein (HEK293 HCP) ELISA kit, G2 | |
E. coli Host Cell Protein (E. coli HCP) ELISA kit, G3 | |
Pichia Pastoris Host Cell Protein (PP HCP) ELISA kit, G3 | |
HP-H0023-3 | Hansenula Polymorpha Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
SC-H0024-3 | Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
SF-H0025-3 | Spodoptera Frugiperda 9 Host Cell Protein ELISA kit, G3 |
Medium Residues Detection kits | |
Protein A ELISA Kit (Boiling) | |
Protein A ELISA Kit | |
Mouse Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Bovine Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Human Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Goat Immunoglobulin G ELISA Kit | |
Kanamycin ELISA Kit | |
Protein L ELISA Kit | |
NEGEP1271 | Protein G ELISA Kit |
Bovine Serum Albumin ELISA Kit | |
Human Serum Albumin ELISA Kit | |
Dextran Sulfate Salt Detection kit | |
Host Cell DNA Detection kits (HCD) | |
NS0 Host Cell DNA (NS0 HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
E.coli Host Cell DNA (E.coli HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
Vero Host Cell DNA (Vero HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
HEK293 Host Cell DNA (HEK293 HCD) Residue Detection kit | |
CHO Host Cell DNA (CHO HCD) Residue Detection Kit | |
Pichia Pastoris Host Cell DNA (PP HCD) Residue Detection Kit | |
Magnetic Residual DNA Sample Preparation Kit | |
Host Cell Protein Antibodies | |
CHO Host Cell Protein G3 Antibody | |
CHO Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody | |
E.coli Host Cell Protein G3 Antibody | |
PH-E0021-2-Ab | Pichia Yeast Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody |
HEK293 Host Cell Protein G2 Antibody | |
Buffer Products | |
CG-H0100 | HCP ELISA buffer |
Protein L ELISA buffer | |